Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of len...
Start Learning for Free
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum...
To complete the vertical circle 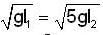
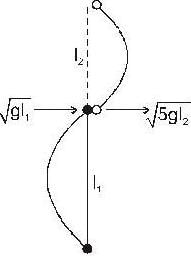
l1/l2 = 5
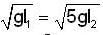

l1/l2 = 5
Most Upvoted Answer
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum...
Analysis:
To solve this problem, we will use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy and the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
1. Conservation of mechanical energy:
The bob at the highest point has potential energy (mgh) and kinetic energy (1/2 mv²). As it completes a full circle, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. Therefore, the total mechanical energy of the bob remains constant throughout its motion.
2. Conservation of linear momentum:
Before the collision, the first bob has a linear momentum (mv) and the second bob has zero linear momentum as it is at rest. After the collision, the linear momentum is conserved, so the first bob will have zero linear momentum and the second bob will acquire a linear momentum (mv).
Derivation:
Let's assume the minimum velocity required to complete a full circle for the first bob is v1, and for the second bob after the collision is v2. Also, let's assume the ratio l1/l2 is x.
1. Conservation of mechanical energy:
At the highest point, the potential energy is maximum and the kinetic energy is zero. Therefore, we can write the equation as:
mgh + 0 = 0 + (1/2) mv1²
2. Conservation of linear momentum:
Before the collision:
mv1 + 0 = 0 + 0
After the collision:
0 + 0 = 0 + mv2
Applying the principle of conservation of mechanical energy:
mgh = (1/2) mv1²
Applying the principle of conservation of linear momentum:
mv1 = mv2
Canceling the mass (m) from both equations:
gh = (1/2) v1²
v1 = 2gh
v2 = v1 = 2gh
Substituting the value of v1 and v2 in terms of x:
v2 = 2gh = 2gxh/5h = 2gx/5
Comparing the expressions for v2:
v2 = 2gx/5
v2 = 2gh
Since the expressions for v2 are equal, we can equate them:
2gx/5 = 2gh
Simplifying the equation:
gx/5 = gh
Canceling the height (h) from both sides:
x/5 = 1
x = 5
Therefore, the ratio l1/l2 is 5.
To solve this problem, we will use the principle of conservation of mechanical energy and the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
1. Conservation of mechanical energy:
The bob at the highest point has potential energy (mgh) and kinetic energy (1/2 mv²). As it completes a full circle, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. Therefore, the total mechanical energy of the bob remains constant throughout its motion.
2. Conservation of linear momentum:
Before the collision, the first bob has a linear momentum (mv) and the second bob has zero linear momentum as it is at rest. After the collision, the linear momentum is conserved, so the first bob will have zero linear momentum and the second bob will acquire a linear momentum (mv).
Derivation:
Let's assume the minimum velocity required to complete a full circle for the first bob is v1, and for the second bob after the collision is v2. Also, let's assume the ratio l1/l2 is x.
1. Conservation of mechanical energy:
At the highest point, the potential energy is maximum and the kinetic energy is zero. Therefore, we can write the equation as:
mgh + 0 = 0 + (1/2) mv1²
2. Conservation of linear momentum:
Before the collision:
mv1 + 0 = 0 + 0
After the collision:
0 + 0 = 0 + mv2
Applying the principle of conservation of mechanical energy:
mgh = (1/2) mv1²
Applying the principle of conservation of linear momentum:
mv1 = mv2
Canceling the mass (m) from both equations:
gh = (1/2) v1²
v1 = 2gh
v2 = v1 = 2gh
Substituting the value of v1 and v2 in terms of x:
v2 = 2gh = 2gxh/5h = 2gx/5
Comparing the expressions for v2:
v2 = 2gx/5
v2 = 2gh
Since the expressions for v2 are equal, we can equate them:
2gx/5 = 2gh
Simplifying the equation:
gx/5 = gh
Canceling the height (h) from both sides:
x/5 = 1
x = 5
Therefore, the ratio l1/l2 is 5.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1, is give a minimum velocity required to complete a full circle in the verticle plane. At the highest point, it collides elastically with another bob of mass m suspended by a string of length l2, which is initially at rest. Both the strings are mass-less and inextensible. If the second bob, after collision acquires the minimum speed required to complete a full circle in verticle plane, the ration l1/l2 is ...Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















