Physics Exam > Physics Questions > A balloon having massmis filled with gas and ...
Start Learning for Free
A balloon having mass m is filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/s with respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]
Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy...
Neglecting gravity
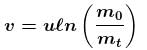
u = ejection velocity w.r.t. balloon
m0 = initial mass
m1 = mass at any time t.
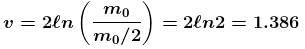
The correct answer is: 1.386
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy...
The velocity of the balloon can be determined using the principle of conservation of momentum.
1. Initial State:
- The balloon is initially held in the hands of a boy.
- The balloon has a certain mass and is filled with gas.
- The gas inside the balloon is at rest with respect to the balloon.
- The velocity of the balloon is zero.
2. Release of Gas:
- When the gas starts coming out of the balloon with a constant rate, it exerts a backward force on the balloon according to Newton's third law of motion.
- The rate at which the gas is being ejected is constant, which means the mass of the gas is reducing at a constant rate.
- According to the principle of conservation of momentum, the change in momentum of the gas must be equal and opposite to the change in momentum of the balloon.
3. Change in Momentum:
- As the gas is being ejected from the balloon, its momentum is decreasing.
- The momentum of the ejected gas is given by the product of its mass and velocity, which is constant at 2 m/s with respect to the balloon.
- The change in momentum of the gas is equal to the mass of the gas multiplied by the change in velocity.
- Since the velocity of the gas is constant, the change in velocity is zero, and therefore the change in momentum of the gas is also zero.
4. Conservation of Momentum:
- The change in momentum of the gas is equal and opposite to the change in momentum of the balloon.
- The mass of the balloon remains constant as the gas is being ejected, so the change in momentum of the balloon is zero.
- This means that the momentum of the balloon remains constant throughout the process.
5. Velocity of the Balloon:
- Since the momentum of the balloon remains constant, and momentum is given by the product of mass and velocity, the velocity of the balloon remains constant as well.
- When the mass of the gas is reduced to half, the momentum of the gas is also reduced to half.
- The momentum of the gas is equal to the mass of the gas multiplied by the velocity of the gas.
- So, if the mass of the gas is reduced to half, the velocity of the gas must also be reduced to half.
- Therefore, the velocity of the balloon when the mass of the gas is reduced to half is half of the initial velocity of the gas, which is 1 m/s.
6. Final Answer:
- The velocity of the balloon when the mass of the gas is reduced to half is 1 m/s.
1. Initial State:
- The balloon is initially held in the hands of a boy.
- The balloon has a certain mass and is filled with gas.
- The gas inside the balloon is at rest with respect to the balloon.
- The velocity of the balloon is zero.
2. Release of Gas:
- When the gas starts coming out of the balloon with a constant rate, it exerts a backward force on the balloon according to Newton's third law of motion.
- The rate at which the gas is being ejected is constant, which means the mass of the gas is reducing at a constant rate.
- According to the principle of conservation of momentum, the change in momentum of the gas must be equal and opposite to the change in momentum of the balloon.
3. Change in Momentum:
- As the gas is being ejected from the balloon, its momentum is decreasing.
- The momentum of the ejected gas is given by the product of its mass and velocity, which is constant at 2 m/s with respect to the balloon.
- The change in momentum of the gas is equal to the mass of the gas multiplied by the change in velocity.
- Since the velocity of the gas is constant, the change in velocity is zero, and therefore the change in momentum of the gas is also zero.
4. Conservation of Momentum:
- The change in momentum of the gas is equal and opposite to the change in momentum of the balloon.
- The mass of the balloon remains constant as the gas is being ejected, so the change in momentum of the balloon is zero.
- This means that the momentum of the balloon remains constant throughout the process.
5. Velocity of the Balloon:
- Since the momentum of the balloon remains constant, and momentum is given by the product of mass and velocity, the velocity of the balloon remains constant as well.
- When the mass of the gas is reduced to half, the momentum of the gas is also reduced to half.
- The momentum of the gas is equal to the mass of the gas multiplied by the velocity of the gas.
- So, if the mass of the gas is reduced to half, the velocity of the gas must also be reduced to half.
- Therefore, the velocity of the balloon when the mass of the gas is reduced to half is half of the initial velocity of the gas, which is 1 m/s.
6. Final Answer:
- The velocity of the balloon when the mass of the gas is reduced to half is 1 m/s.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Question Description
A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer?.
A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A balloon having massmis filled with gas and is held in hands of a boy. Then suddenly it get released and gas start coming out of it with a constant rate. The velocities of the ejected gases is also constant 2m/swith respect to the balloon. Find out the velocity of the balloon when the mass of gas is reduced to half. [Effect of atmosphere and gravity is neglected]Correct answer is '1.386'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















