Physics Exam > Physics Questions > Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier...
Start Learning for Free
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term?
Most Upvoted Answer
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load res...
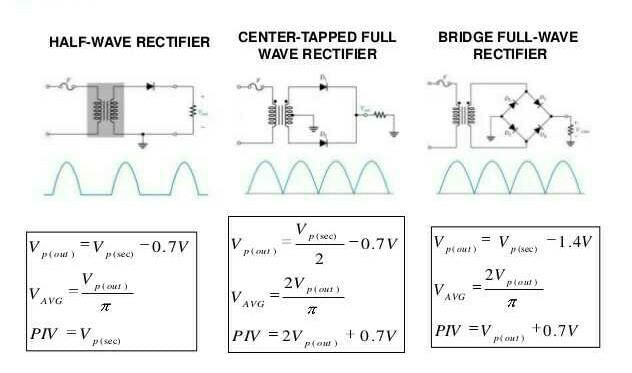
Half Wave Rectifier:
The ripple factor of a half wave rectifier is a measure of the amount of AC voltage present in the rectified output. It is given by the ratio of the root mean square (rms) value of the ripple voltage to the DC output voltage.
Formula:
Ripple factor (γ) = Vrms / Vdc
where:
Vrms is the rms value of the ripple voltage
Vdc is the average DC output voltage
Frequency:
The ripple voltage is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC input signal. As the frequency increases, the ripple voltage also increases. This can be understood by considering the fact that a higher frequency results in a shorter time duration for each half cycle, leading to less time for the capacitor to charge and discharge. Consequently, the ripple voltage becomes more significant.
Load Resistance:
The ripple voltage is inversely proportional to the load resistance in a half wave rectifier. As the load resistance increases, the ripple voltage decreases. This is because a higher load resistance allows the capacitor to discharge more slowly, resulting in a smaller ripple voltage.
Therefore, the ripple factor of a half wave rectifier is influenced by both the frequency and the load resistance.
Full Wave Rectifier:
The ripple factor of a full wave rectifier is also a measure of the amount of AC voltage present in the rectified output. However, in a full wave rectifier, the ripple frequency is twice the input AC frequency, and the ripple factor is defined slightly differently.
Formula:
Ripple factor (γ) = Vrms / Vdc
where:
Vrms is the rms value of the ripple voltage
Vdc is the average DC output voltage
Frequency:
In a full wave rectifier, the ripple frequency is twice the input AC frequency. This means that for the same input frequency, the ripple frequency is higher in a full wave rectifier compared to a half wave rectifier. As a result, the ripple voltage is reduced, and the output is smoother.
Load Resistance:
Similar to a half wave rectifier, the ripple voltage in a full wave rectifier is inversely proportional to the load resistance. A higher load resistance allows the capacitor to discharge more slowly, resulting in a smaller ripple voltage.
Therefore, the ripple factor of a full wave rectifier is also influenced by both the frequency and the load resistance.
The ripple factor of a half wave rectifier is a measure of the amount of AC voltage present in the rectified output. It is given by the ratio of the root mean square (rms) value of the ripple voltage to the DC output voltage.
Formula:
Ripple factor (γ) = Vrms / Vdc
where:
Vrms is the rms value of the ripple voltage
Vdc is the average DC output voltage
Frequency:
The ripple voltage is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC input signal. As the frequency increases, the ripple voltage also increases. This can be understood by considering the fact that a higher frequency results in a shorter time duration for each half cycle, leading to less time for the capacitor to charge and discharge. Consequently, the ripple voltage becomes more significant.
Load Resistance:
The ripple voltage is inversely proportional to the load resistance in a half wave rectifier. As the load resistance increases, the ripple voltage decreases. This is because a higher load resistance allows the capacitor to discharge more slowly, resulting in a smaller ripple voltage.
Therefore, the ripple factor of a half wave rectifier is influenced by both the frequency and the load resistance.
Full Wave Rectifier:
The ripple factor of a full wave rectifier is also a measure of the amount of AC voltage present in the rectified output. However, in a full wave rectifier, the ripple frequency is twice the input AC frequency, and the ripple factor is defined slightly differently.
Formula:
Ripple factor (γ) = Vrms / Vdc
where:
Vrms is the rms value of the ripple voltage
Vdc is the average DC output voltage
Frequency:
In a full wave rectifier, the ripple frequency is twice the input AC frequency. This means that for the same input frequency, the ripple frequency is higher in a full wave rectifier compared to a half wave rectifier. As a result, the ripple voltage is reduced, and the output is smoother.
Load Resistance:
Similar to a half wave rectifier, the ripple voltage in a full wave rectifier is inversely proportional to the load resistance. A higher load resistance allows the capacitor to discharge more slowly, resulting in a smaller ripple voltage.
Therefore, the ripple factor of a full wave rectifier is also influenced by both the frequency and the load resistance.
Community Answer
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load res...

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term?
Question Description
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term?.
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term?.
Solutions for Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term?, a detailed solution for Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? has been provided alongside types of Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ripple factor of half and full wave rectifier in frequency or load resistance term? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















