NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Flowchart on Immunity?
Start Learning for Free
Flowchart on Immunity?
Community Answer
Flowchart on Immunity?
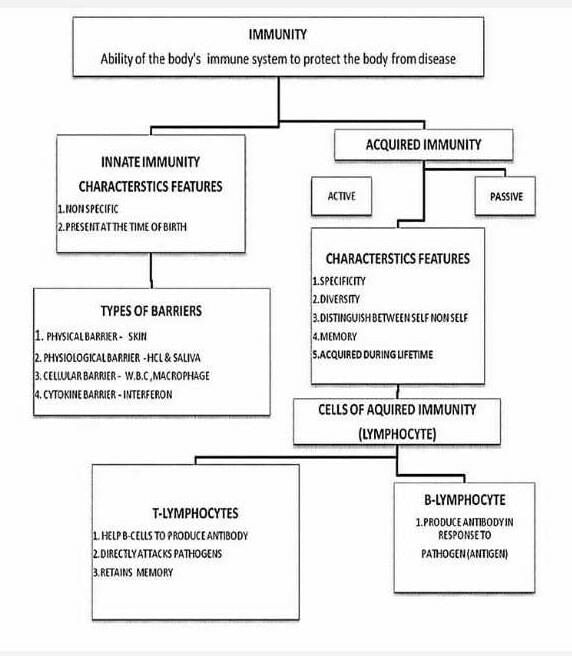
Flowchart on Immunity:
Immunity is the ability of an organism to resist or defend against potentially harmful foreign substances or pathogens. It involves a complex network of cells, tissues, and molecules that work together to protect the body from infections and diseases. A flowchart can help visualize the different components and processes involved in immunity.
The flowchart on immunity can be divided into the following sections:
1. Recognition of Pathogens:
- The immune system first needs to recognize the presence of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, in the body.
- This recognition can occur through various mechanisms, including the detection of specific molecules on the surface of pathogens called antigens.
2. Activation of Immune Response:
- Once the pathogens are recognized, the immune system is activated to mount a response.
- This can involve the release of chemical signals called cytokines, which recruit immune cells to the site of infection.
3. Cellular Immune Response:
- The immune system has two main branches: the cellular or cell-mediated immune response and the humoral immune response.
- In the cellular immune response, specialized immune cells called T cells play a crucial role.
- T cells can directly kill infected cells or release cytokines to activate other immune cells.
4. Humoral Immune Response:
- The humoral immune response involves the production of antibodies by B cells.
- Antibodies are proteins that can bind to specific antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells or neutralizing their harmful effects.
5. Memory Response:
- After an infection is cleared, some immune cells called memory cells persist in the body.
- These memory cells "remember" the specific pathogens they have encountered before, allowing for a faster and more efficient immune response upon re-infection.
6. Primary and Secondary Immune Response:
- The primary immune response occurs during the first exposure to a pathogen, and it takes time for the immune system to mount an effective response.
- The secondary immune response, on the other hand, occurs upon re-exposure to the same pathogen and is faster and stronger due to the presence of memory cells.
7. Immune System Disorders:
- Sometimes, the immune system can malfunction, leading to immune system disorders.
- Examples include autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, and immunodeficiency disorders, where the immune system is weakened or impaired.
Overall, the flowchart on immunity helps illustrate the different steps and components involved in the immune response, highlighting the complexity and interconnectedness of the immune system.
Immunity is the ability of an organism to resist or defend against potentially harmful foreign substances or pathogens. It involves a complex network of cells, tissues, and molecules that work together to protect the body from infections and diseases. A flowchart can help visualize the different components and processes involved in immunity.
The flowchart on immunity can be divided into the following sections:
1. Recognition of Pathogens:
- The immune system first needs to recognize the presence of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, in the body.
- This recognition can occur through various mechanisms, including the detection of specific molecules on the surface of pathogens called antigens.
2. Activation of Immune Response:
- Once the pathogens are recognized, the immune system is activated to mount a response.
- This can involve the release of chemical signals called cytokines, which recruit immune cells to the site of infection.
3. Cellular Immune Response:
- The immune system has two main branches: the cellular or cell-mediated immune response and the humoral immune response.
- In the cellular immune response, specialized immune cells called T cells play a crucial role.
- T cells can directly kill infected cells or release cytokines to activate other immune cells.
4. Humoral Immune Response:
- The humoral immune response involves the production of antibodies by B cells.
- Antibodies are proteins that can bind to specific antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells or neutralizing their harmful effects.
5. Memory Response:
- After an infection is cleared, some immune cells called memory cells persist in the body.
- These memory cells "remember" the specific pathogens they have encountered before, allowing for a faster and more efficient immune response upon re-infection.
6. Primary and Secondary Immune Response:
- The primary immune response occurs during the first exposure to a pathogen, and it takes time for the immune system to mount an effective response.
- The secondary immune response, on the other hand, occurs upon re-exposure to the same pathogen and is faster and stronger due to the presence of memory cells.
7. Immune System Disorders:
- Sometimes, the immune system can malfunction, leading to immune system disorders.
- Examples include autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, and immunodeficiency disorders, where the immune system is weakened or impaired.
Overall, the flowchart on immunity helps illustrate the different steps and components involved in the immune response, highlighting the complexity and interconnectedness of the immune system.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Flowchart on Immunity? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flowchart on Immunity? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flowchart on Immunity?.
Flowchart on Immunity? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flowchart on Immunity? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flowchart on Immunity?.
Solutions for Flowchart on Immunity? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Flowchart on Immunity? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Flowchart on Immunity?, a detailed solution for Flowchart on Immunity? has been provided alongside types of Flowchart on Immunity? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Flowchart on Immunity? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.