NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Flowchart on "plant tissues"?
Start Learning for Free
Flowchart on "plant tissues"?
Community Answer
Flowchart on "plant tissues"?
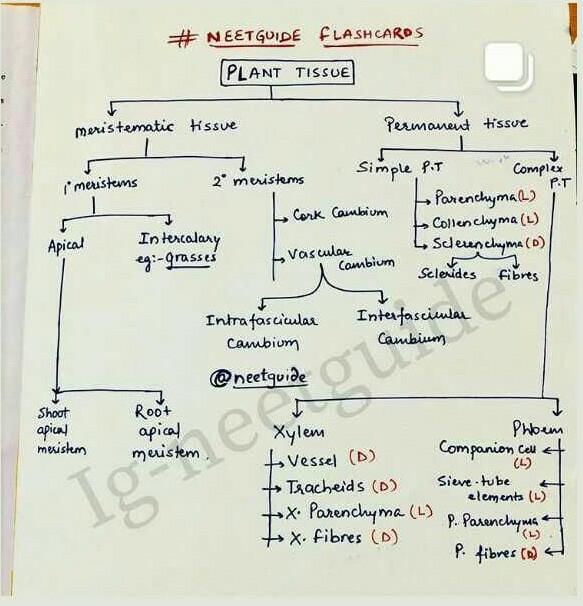
Plant Tissues:
Plant tissues are groups of cells that are specialized to perform specific functions within a plant. There are several types of plant tissues, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. These tissues work together to support the growth, development, and survival of plants.
Types of Plant Tissues:
There are three main types of plant tissues:
1. Meristematic Tissue:
- In plants, growth occurs continuously throughout their lifespan, and this is made possible by meristematic tissue.
- Meristematic tissue is responsible for cell division and growth in plants.
- It is located at the tips of stems and roots, as well as in regions of active growth such as the cambium.
- Meristematic tissue consists of small, undifferentiated cells that have the ability to divide and differentiate into other types of plant tissues.
2. Permanent Tissue:
- Once cells in the meristematic tissue divide and differentiate, they become part of the permanent tissue.
- Permanent tissue can be further classified into three types: simple, complex, and special.
- Simple permanent tissue consists of cells that are similar in structure and function.
- Complex permanent tissue consists of different types of cells that work together to perform specific functions.
- Special permanent tissue is unique to certain plant organs and performs specialized functions.
3. Protective Tissue:
- Protective tissue is responsible for protecting the plant from external factors such as physical damage, pathogens, and water loss.
- Epidermis is the outermost protective tissue layer in leaves, stems, and roots, and it helps in reducing water loss.
- Cork is another type of protective tissue that forms the outer bark of woody plants and protects them from mechanical and environmental damage.
Functions of Plant Tissues:
Plant tissues have various functions that are essential for the growth and survival of plants:
1. Transport:
- Vascular tissues, such as xylem and phloem, are responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
- Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, while phloem transports sugars and other organic molecules from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
2. Support:
- Plant tissues, such as collenchyma and sclerenchyma, provide structural support to the plant.
- Collenchyma tissues are flexible and provide support to actively growing regions.
- Sclerenchyma tissues are rigid and provide mechanical support to mature plant parts.
3. Photosynthesis:
- Mesophyll tissues in leaves contain chloroplasts and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
4. Storage:
- Parenchyma tissues in roots, stems, and fruits store nutrients, water, and other essential substances.
In conclusion, plant tissues play a crucial role in the growth, development, and survival of plants. They are responsible for various functions such as cell division, transport of nutrients, support, protection, photosynthesis, and storage. Understanding the different types and functions of plant tissues is essential for studying plant biology and understanding how plants function.
Plant tissues are groups of cells that are specialized to perform specific functions within a plant. There are several types of plant tissues, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. These tissues work together to support the growth, development, and survival of plants.
Types of Plant Tissues:
There are three main types of plant tissues:
1. Meristematic Tissue:
- In plants, growth occurs continuously throughout their lifespan, and this is made possible by meristematic tissue.
- Meristematic tissue is responsible for cell division and growth in plants.
- It is located at the tips of stems and roots, as well as in regions of active growth such as the cambium.
- Meristematic tissue consists of small, undifferentiated cells that have the ability to divide and differentiate into other types of plant tissues.
2. Permanent Tissue:
- Once cells in the meristematic tissue divide and differentiate, they become part of the permanent tissue.
- Permanent tissue can be further classified into three types: simple, complex, and special.
- Simple permanent tissue consists of cells that are similar in structure and function.
- Complex permanent tissue consists of different types of cells that work together to perform specific functions.
- Special permanent tissue is unique to certain plant organs and performs specialized functions.
3. Protective Tissue:
- Protective tissue is responsible for protecting the plant from external factors such as physical damage, pathogens, and water loss.
- Epidermis is the outermost protective tissue layer in leaves, stems, and roots, and it helps in reducing water loss.
- Cork is another type of protective tissue that forms the outer bark of woody plants and protects them from mechanical and environmental damage.
Functions of Plant Tissues:
Plant tissues have various functions that are essential for the growth and survival of plants:
1. Transport:
- Vascular tissues, such as xylem and phloem, are responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
- Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, while phloem transports sugars and other organic molecules from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
2. Support:
- Plant tissues, such as collenchyma and sclerenchyma, provide structural support to the plant.
- Collenchyma tissues are flexible and provide support to actively growing regions.
- Sclerenchyma tissues are rigid and provide mechanical support to mature plant parts.
3. Photosynthesis:
- Mesophyll tissues in leaves contain chloroplasts and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
4. Storage:
- Parenchyma tissues in roots, stems, and fruits store nutrients, water, and other essential substances.
In conclusion, plant tissues play a crucial role in the growth, development, and survival of plants. They are responsible for various functions such as cell division, transport of nutrients, support, protection, photosynthesis, and storage. Understanding the different types and functions of plant tissues is essential for studying plant biology and understanding how plants function.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Flowchart on "plant tissues"? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flowchart on "plant tissues"? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flowchart on "plant tissues"?.
Flowchart on "plant tissues"? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flowchart on "plant tissues"? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flowchart on "plant tissues"?.
Solutions for Flowchart on "plant tissues"? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Flowchart on "plant tissues"? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Flowchart on "plant tissues"?, a detailed solution for Flowchart on "plant tissues"? has been provided alongside types of Flowchart on "plant tissues"? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Flowchart on "plant tissues"? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.