JEE Exam > JEE Questions > If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a c...
Start Learning for Free
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.
Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.
Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume)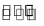 Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.
Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.
Solid (lower volume)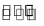 Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomes
Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomes
high.
Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.
Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume)
Solid (lower volume)
high.
(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).
KCI + aq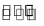 KCl(aq) – heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.
KCl(aq) – heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.
KOH + aq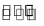 KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.
KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.
Effect of temperature : Le-Chatelier's principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Van't Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:
KCI + aq
KOH + aq
Effect of temperature : Le-Chatelier's principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Van't Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:
Q.
The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K being the equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is then correct ?
- a)The reaction is endothermic in nature
- b)The reaction will be exothermic in nature
- c)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperature
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the f...
Since the slope of the straight line graph between log and 1/2
is positive, ΔHreaction would be negative, i.e.,
the forward reaction would be exothermic.
is positive, ΔHreaction would be negative, i.e.,
the forward reaction would be exothermic.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If a systemat equilibrium is subjected to a change of any one of the factors such as concentration, pressure temperature, the system adjusts itself in such a way as to (Nulify) the effect of that change.Change of pressure : If a system in equilibrium consists of gases, then the concentrations of all the components can be altered by changing the pressure. When the pressure on the system is increased, the volume decreases proportionately. The total number of moles per unit volume will now be more and the equilibirum will shift in the direction in which there is decrease in number of moles ice., towards the direction in which there is decrease in volume.Effect of pressure on melting point : There are two types of solids : (a) Solids whose volume decreases on melting, egg., ice, diamond, carborundum, magnesium nitride and quartz Solid (higher volume) Liquid (lower volume) Them process of melting is facilitated at high pressure, thus melting point is lowered. .(b) Solids whose volume increase on melting, e.g., Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, etc.Solid (lower volume) Liquid (higher volume) In this case the process of melting become difficult at high pressure; thus melting point becomeshigh.(c) Solubility of substances : When solid substance are dissolved in water, either heat is evolved (exothermic) or heat is absorbed (endothermic).KCI + aq KCl(aq) heat In such cases, solubility increase with increase in temperature. Consider the case of KOH; when this is dissolved, heat is evolved.KOH + aq KOH(aq) + heat In such cases, solubility decrease with increase in temperature. (d) Solubility of gases in liquids : When a gas dissolves in liquid, there is decrease in volume. Thus, increase of pressure will favour the dissolution of gas in liquid.Effect of temperature : Le-Chateliers principle predicts a system at equilibrium will tend to shift in the endothermic direction when temperature is raised, for then energy is absorbed as heat and the rise in temperature is opposed. Conversely, an equilibrium will shift in the exothermic direction if the temperature is lowered, for then that energy is released and the reduction in temperature is opposed. Vant Hoff equation shows the dependence of equilibrium constant K on temperature as:Q.The plot of log K against 1 -- is a straight line with positive slope (K beingthe equilibrium constant of a reaction), which of the following is thencorrect ?a) The reaction is endothermic in natureb) The reaction will be exothermic in naturec)The reaction goes to farther extent on raising the temperatured) None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























