JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The rate of chemical reaction at a particular...
Start Learning for Free
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB → products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.
EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB <=> cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi , concentrations of reactants & products at equilibrium are related by
EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB <=> cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi , concentrations of reactants & products at equilibrium are related by
where all the concentrations are expressed in mole/liter.
In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.
If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).
If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).
The values of expression 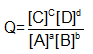
at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q > Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q < Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibrium
q.
Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C is
- a)1/3M
- b)2/3M
- c)4/3M
- d)1/2M
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportio...

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The rate of chemical reaction at a particular temperature is proportional to the product of the molar concentration of reactants with each concentration term raised to the power equal to the number of molecules of the respective reactant taking part in the reaction. aA + bB products, rate of reaction a [Aka [Bib = k [Aka [Bib, where k is the rate constant of the reaction.EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT (k) For a general reaction aA + bB = cC + dD, forward rate rf = kf [A]a [B]b, backward rate rb = kb [Cicpyi ,concentrations of reactants products at equilibrium are related bywhere all theconcentrations are expressed in mole/liter.In the expression of equilibrium constant those components are kept whose concentration changes with time.If equilibrium is estabilished by taking all the components in the reaction then to predict the direction of reactions we calculate the reaction quotient (Q).The values of expression at any time during reaction is called reaction quotient if Q Kc reaction proceed in backward direction until equilibrium in reached if Q Kc reaction will proceed in forward direction until equilibrium is established if Q = KC Reaction is at equilibriumq.Above homogeneous reaction is carried out in a 2 litre container at a particular temperature by taking 1 mole each of A, B, C and D respectively. If Kc for the reaction is then equilibrium concentration of C isa)1/3Mb)2/3Mc)4/3Md)1/2MCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























