JEE Exam > JEE Questions > PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit...
Start Learning for Free
PARAGRAPH–1
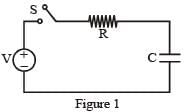
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to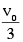 and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to
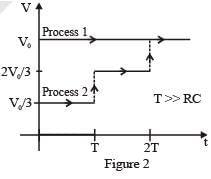
and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to 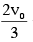 without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.
without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to
Q. In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Pro...
For process (1)
Charge on capacitor =
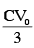
energy stored in capacitor =
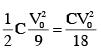
work done by battery =
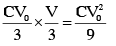
Heat loss =
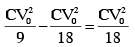
Charge on capacitor =
energy stored in capacitor =
work done by battery =
Heat loss =
For process (2)
Charge on capacitor =
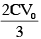
Extra charge flow through battery =
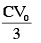
Work done by battery :

Final energy store in capacitor :
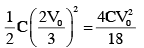
energy store in process 2 :
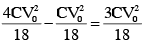
Heat loss in process (2) = work done by battery in process (2) – energy store in capacitor process (2)
Charge on capacitor =
Extra charge flow through battery =
Work done by battery :
Final energy store in capacitor :
energy store in process 2 :
Heat loss in process (2) = work done by battery in process (2) – energy store in capacitor process (2)
For process (3)
Charge on capacitor = CV0
extra charge flow through battery :
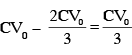
work done by battery in this process :
Charge on capacitor = CV0
extra charge flow through battery :
work done by battery in this process :
find energy store in capacitor :
energy stored in this process :

Now total heat loss (ED) :
final energy store in capacitor :
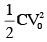
so we can say that ED =
so we can say that ED =

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice PARAGRAPH–1Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging timeT >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to without discharging the capacitor and again maintained fora time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitoris charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.Q.In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















