Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > every notes of chapter nationalism in india R...
Start Learning for Free
every notes of chapter nationalism in india
?Most Upvoted Answer
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter...
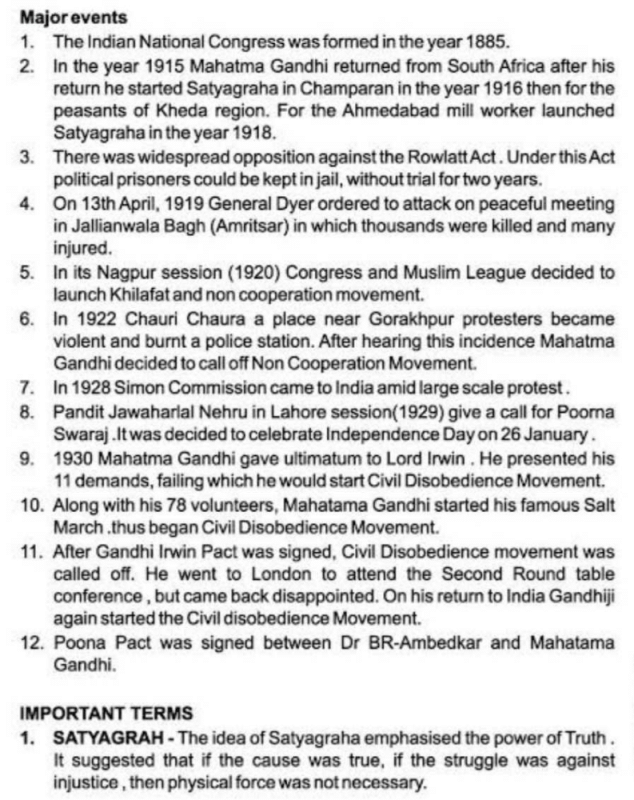
Nationalism in India:
Introduction:
- The idea of nationalism in India was shaped during the struggle for independence from British rule.
- It was based on the principles of unity, self-rule, and the restoration of India's cultural identity.
Factors contributing to the rise of nationalism:
- British colonial policies, such as the partition of Bengal in 1905 and the implementation of the Rowlatt Act in 1919, created resentment among Indians.
- The influence of western education and ideas of democracy and equality also contributed to the rise of nationalism.
- Leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Subhas Chandra Bose played a significant role in mobilizing the masses.
The role of political parties:
- The Indian National Congress, founded in 1885, was the most prominent political party working towards independence.
- Other parties such as the Muslim League and the Communist Party of India also played a role in the freedom struggle.
Methods of protest:
- Non-violent methods such as civil disobedience, boycotts, and strikes were used to protest against British rule.
- The Salt Satyagraha, led by Mahatma Gandhi, was a significant movement that highlighted the power of non-violent resistance.
The impact of nationalism:
- The struggle for independence in India inspired other colonized nations to fight for their freedom.
- The formation of the Indian Constitution in 1950, which established India as a democratic republic, was a significant achievement of the nationalist movement.
French Revolution:
Introduction:
- The French Revolution was a period of radical political and social upheaval in France from 1789 to 1799.
- It was characterized by the overthrow of the monarchy, the establishment of a republic, and the Reign of Terror.
Causes of the French Revolution:
- The French monarchy was facing financial difficulties due to wars and extravagance.
- The French society was divided into three estates, with the third estate, which comprised the common people, bearing the burden of taxes and poverty.
Events of the French Revolution:
- The storming of the Bastille, a prison symbolizing royal tyranny, on July 14, 1789, marked the beginning of the revolution.
- The Reign of Terror, led by Maximilien Robespierre, was a period of violence and bloodshed, resulting in the execution of thousands of people.
Impact of the French Revolution:
- The French Revolution had a significant impact on the world, inspiring other revolutionary movements and the spread of democratic ideals.
- The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, adopted in 1789, remains a cornerstone of modern democracy and human rights.
Introduction:
- The idea of nationalism in India was shaped during the struggle for independence from British rule.
- It was based on the principles of unity, self-rule, and the restoration of India's cultural identity.
Factors contributing to the rise of nationalism:
- British colonial policies, such as the partition of Bengal in 1905 and the implementation of the Rowlatt Act in 1919, created resentment among Indians.
- The influence of western education and ideas of democracy and equality also contributed to the rise of nationalism.
- Leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Subhas Chandra Bose played a significant role in mobilizing the masses.
The role of political parties:
- The Indian National Congress, founded in 1885, was the most prominent political party working towards independence.
- Other parties such as the Muslim League and the Communist Party of India also played a role in the freedom struggle.
Methods of protest:
- Non-violent methods such as civil disobedience, boycotts, and strikes were used to protest against British rule.
- The Salt Satyagraha, led by Mahatma Gandhi, was a significant movement that highlighted the power of non-violent resistance.
The impact of nationalism:
- The struggle for independence in India inspired other colonized nations to fight for their freedom.
- The formation of the Indian Constitution in 1950, which established India as a democratic republic, was a significant achievement of the nationalist movement.
French Revolution:
Introduction:
- The French Revolution was a period of radical political and social upheaval in France from 1789 to 1799.
- It was characterized by the overthrow of the monarchy, the establishment of a republic, and the Reign of Terror.
Causes of the French Revolution:
- The French monarchy was facing financial difficulties due to wars and extravagance.
- The French society was divided into three estates, with the third estate, which comprised the common people, bearing the burden of taxes and poverty.
Events of the French Revolution:
- The storming of the Bastille, a prison symbolizing royal tyranny, on July 14, 1789, marked the beginning of the revolution.
- The Reign of Terror, led by Maximilien Robespierre, was a period of violence and bloodshed, resulting in the execution of thousands of people.
Impact of the French Revolution:
- The French Revolution had a significant impact on the world, inspiring other revolutionary movements and the spread of democratic ideals.
- The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, adopted in 1789, remains a cornerstone of modern democracy and human rights.
Community Answer
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter...
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution?
Question Description
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution?.
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution?.
Solutions for every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution?, a detailed solution for every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? has been provided alongside types of every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice every notes of chapter nationalism in india Related: Detailed Chapter Notes - French Revolution? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























