Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Questions > function of platelets
Start Learning for Free
function of platelets
Verified Answer
function of platelets
In addition to being the smallest blood cell, platelets are also the lightest. Therefore they are pushed out from the center of flowing blood to the wall of the blood vessel. There they roll along the surface of the vessel wall, which is lined by cells called endothelium. The endothelium is a very special surface, like Teflon, that prevents anything from sticking to it. However when there is an injury or cut, and the endothelial layer is broken, the tough fibers that surround a blood vessel are exposed to the liquid flowing blood. It is the platelets that react first to injury. The tough fibers surrounding the vessel wall, like an envelop, attract platelets like a magnet, stimulate the shape change that is shown in the pictures above, and platelets then clump onto these fibers, providing the initial seal to prevent bleeding, the leak of red blood cells and plasma through the vessel injury.
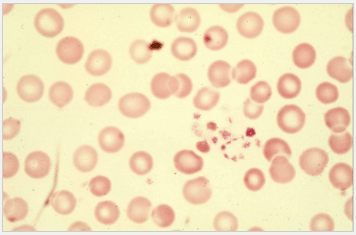
The color photograph is a microscopic picture of a drop of blood spread out onto a glass slide. The magnification is not as high as the pictures above, so the platelets seem very small. It can be seen that as the platelets touch the glass, they begin to stick together forming a long string. This illustrates the basic function of platelets, to stick to any foreign surface and then to stick together. The red blood cells in this picture are normal, with their round shape and their thin center.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
function of platelets
Function of Platelets
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments present in the blood. They play a crucial role in hemostasis, which is the process by which the body stops bleeding after an injury. Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood. Here is a detailed explanation of the functions of platelets:
Formation of Platelet Plug:
- When a blood vessel is injured, platelets are the first responders. They adhere to the damaged area of the blood vessel's wall, forming a temporary platelet plug to prevent further blood loss.
- Platelets release various substances, including clotting factors and chemicals such as serotonin and thromboxane A2. These substances help in vasoconstriction, which narrows the blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the affected area.
Clot Formation:
- Platelets are essential in the formation of blood clots. They aggregate together to form a stable clot, which seals the site of injury.
- The platelet plug acts as a scaffold for the formation of fibrin, a protein that forms a mesh-like structure. Fibrin traps red blood cells and other platelets, forming a stable blood clot.
Release of Growth Factors and Cytokines:
- Platelets contain growth factors and cytokines that play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. Upon activation, platelets release these substances, which stimulate cell division and promote the healing process.
- Growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) promote the growth of new blood vessels and aid in tissue regeneration.
Immune Response:
- Platelets also play a role in the immune response. They can interact with immune cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, enhancing their function in fighting infections.
- Platelets release antimicrobial peptides and chemokines, which attract immune cells to the site of infection or injury.
Removal of Waste Products:
- Platelets contribute to the removal of waste products and cellular debris from the bloodstream. They can engulf and break down bacteria, viruses, and other foreign particles through a process called phagocytosis.
In conclusion, platelets are essential for maintaining normal hemostasis. They form a platelet plug to prevent bleeding, promote clot formation, release growth factors for tissue repair, aid in the immune response, and participate in the removal of waste products. Their multifunctional role highlights their importance in maintaining the integrity of the circulatory system.
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments present in the blood. They play a crucial role in hemostasis, which is the process by which the body stops bleeding after an injury. Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and circulate in the blood. Here is a detailed explanation of the functions of platelets:
Formation of Platelet Plug:
- When a blood vessel is injured, platelets are the first responders. They adhere to the damaged area of the blood vessel's wall, forming a temporary platelet plug to prevent further blood loss.
- Platelets release various substances, including clotting factors and chemicals such as serotonin and thromboxane A2. These substances help in vasoconstriction, which narrows the blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the affected area.
Clot Formation:
- Platelets are essential in the formation of blood clots. They aggregate together to form a stable clot, which seals the site of injury.
- The platelet plug acts as a scaffold for the formation of fibrin, a protein that forms a mesh-like structure. Fibrin traps red blood cells and other platelets, forming a stable blood clot.
Release of Growth Factors and Cytokines:
- Platelets contain growth factors and cytokines that play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. Upon activation, platelets release these substances, which stimulate cell division and promote the healing process.
- Growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) promote the growth of new blood vessels and aid in tissue regeneration.
Immune Response:
- Platelets also play a role in the immune response. They can interact with immune cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, enhancing their function in fighting infections.
- Platelets release antimicrobial peptides and chemokines, which attract immune cells to the site of infection or injury.
Removal of Waste Products:
- Platelets contribute to the removal of waste products and cellular debris from the bloodstream. They can engulf and break down bacteria, viruses, and other foreign particles through a process called phagocytosis.
In conclusion, platelets are essential for maintaining normal hemostasis. They form a platelet plug to prevent bleeding, promote clot formation, release growth factors for tissue repair, aid in the immune response, and participate in the removal of waste products. Their multifunctional role highlights their importance in maintaining the integrity of the circulatory system.
Attention Class 7 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 7 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 7.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Similar Class 7 Doubts
function of platelets
Question Description
function of platelets for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about function of platelets covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for function of platelets.
function of platelets for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about function of platelets covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for function of platelets.
Solutions for function of platelets in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 7.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of function of platelets defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
function of platelets, a detailed solution for function of platelets has been provided alongside types of function of platelets theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice function of platelets tests, examples and also practice Class 7 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























