Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Which of the following molecule exhibits conf...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?
- a)CH3OH
- b)CF4
- c)CH4
- d)CH2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)C...
The correct answer is option A.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)C...
Conformational isomerism occurs when a molecule can adopt different spatial arrangements due to rotation around a single bond. Among the given options, only CH4 exhibits conformational isomerism.
Explanation:
- Conformational isomerism arises due to the ability of a molecule to rotate around a single bond without breaking it. The different arrangements of atoms resulting from this rotation are called conformers or conformations.
- In the case of CH4, it is a tetrahedral molecule with four hydrogen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. The carbon-hydrogen bonds can rotate freely without breaking, allowing for different spatial arrangements of the hydrogen atoms.
- The rotation can occur around any of the carbon-hydrogen bonds, resulting in different conformations. The different conformations are represented by Newman projections, which show the molecule viewed along the carbon-hydrogen bond axis.
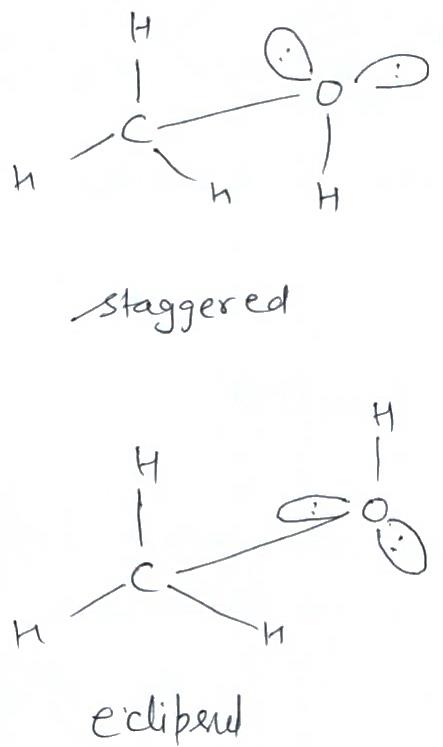
- For example, CH4 can adopt different conformations where the hydrogen atoms are positioned at different angles relative to each other. These conformations are called staggered and eclipsed conformations.
- In the staggered conformation, the hydrogen atoms are positioned as far apart as possible, resulting in lower steric hindrance and more stable conformation. This conformation is energetically favored.
- In the eclipsed conformation, the hydrogen atoms are positioned directly opposite each other, resulting in higher steric hindrance and less stable conformation. This conformation is energetically disfavored.
- The ability of CH4 to freely rotate around its carbon-hydrogen bonds allows it to interconvert between different conformations, resulting in conformational isomerism.
In conclusion, CH4 is the only molecule among the given options that exhibits conformational isomerism due to the rotation of its carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Explanation:
- Conformational isomerism arises due to the ability of a molecule to rotate around a single bond without breaking it. The different arrangements of atoms resulting from this rotation are called conformers or conformations.
- In the case of CH4, it is a tetrahedral molecule with four hydrogen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. The carbon-hydrogen bonds can rotate freely without breaking, allowing for different spatial arrangements of the hydrogen atoms.
- The rotation can occur around any of the carbon-hydrogen bonds, resulting in different conformations. The different conformations are represented by Newman projections, which show the molecule viewed along the carbon-hydrogen bond axis.
- For example, CH4 can adopt different conformations where the hydrogen atoms are positioned at different angles relative to each other. These conformations are called staggered and eclipsed conformations.
- In the staggered conformation, the hydrogen atoms are positioned as far apart as possible, resulting in lower steric hindrance and more stable conformation. This conformation is energetically favored.
- In the eclipsed conformation, the hydrogen atoms are positioned directly opposite each other, resulting in higher steric hindrance and less stable conformation. This conformation is energetically disfavored.
- The ability of CH4 to freely rotate around its carbon-hydrogen bonds allows it to interconvert between different conformations, resulting in conformational isomerism.
In conclusion, CH4 is the only molecule among the given options that exhibits conformational isomerism due to the rotation of its carbon-hydrogen bonds.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following molecule exhibits conformational isomerism ?a)CH3OHb)CF4c)CH4d)CH2OCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























