Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Questions > what is difference between conduction convect...
Start Learning for Free
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?
Verified Answer
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?
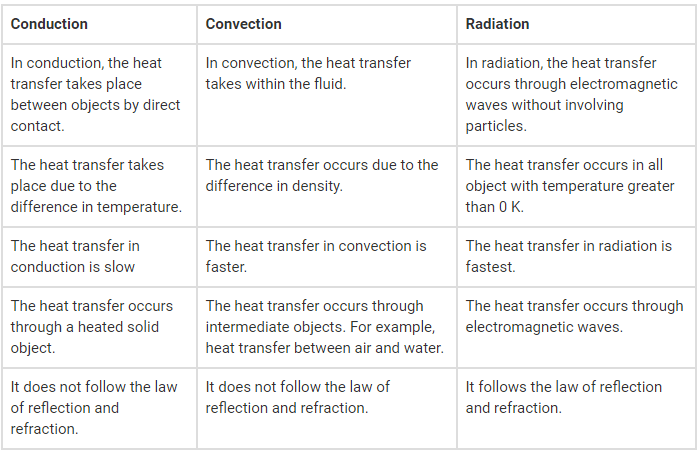
Conduction, convection, and radiation are the three main modes of heat transfer. Each mode operates differently and has unique characteristics. Let's explore each mode in detail:
1. Conduction:
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects or substances that are in physical contact with each other. In this mode, heat energy is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature through molecular collisions. The key points about conduction are:
- Molecular Collisions: Heat is transferred when faster-moving molecules collide with slower-moving molecules, thus transferring their energy.
- Direct Contact: Conduction occurs when objects or substances are in direct contact with each other.
- Conductors and Insulators: The rate of conduction depends on the material's ability to conduct heat. Materials that conduct heat well, such as metals, are called conductors, while materials that resist heat transfer, such as wood or air, are called insulators.
- Examples: When you touch a hot stove, heat is conducted from the stove to your hand. Similarly, a metal spoon in a hot soup becomes hot due to conduction.
2. Convection:
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It occurs due to the circulation of heated particles within a fluid. The key points about convection are:
- Fluid Movement: Convection requires the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) to transfer heat. This movement can occur naturally (natural convection) or through mechanical means (forced convection).
- Density Differences: Convection is driven by density differences caused by temperature variations in the fluid. Hot fluid expands, becomes less dense, and rises, while cooler fluid sinks.
- Examples: Boiling water in a pot involves convection as the hot water rises and cooler water sinks, creating a circulation pattern. Similarly, the heating and cooling of air in a room involve convection currents.
3. Radiation:
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to transfer heat. The key points about radiation are:
- Electromagnetic Waves: Heat is transferred through the emission and absorption of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation.
- No Medium Required: Unlike conduction and convection, radiation can occur in a vacuum or through transparent mediums, as it does not rely on physical contact or particle movement.
- Examples: The warmth you feel from the sunlight is due to radiation. Similarly, a heated metal object radiates heat to its surroundings.
In summary, conduction involves direct contact between objects, convection requires fluid movement, and radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves. These modes of heat transfer play crucial roles in various natural and technological processes, influencing how heat is distributed and transferred in different systems.
1. Conduction:
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects or substances that are in physical contact with each other. In this mode, heat energy is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature through molecular collisions. The key points about conduction are:
- Molecular Collisions: Heat is transferred when faster-moving molecules collide with slower-moving molecules, thus transferring their energy.
- Direct Contact: Conduction occurs when objects or substances are in direct contact with each other.
- Conductors and Insulators: The rate of conduction depends on the material's ability to conduct heat. Materials that conduct heat well, such as metals, are called conductors, while materials that resist heat transfer, such as wood or air, are called insulators.
- Examples: When you touch a hot stove, heat is conducted from the stove to your hand. Similarly, a metal spoon in a hot soup becomes hot due to conduction.
2. Convection:
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It occurs due to the circulation of heated particles within a fluid. The key points about convection are:
- Fluid Movement: Convection requires the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) to transfer heat. This movement can occur naturally (natural convection) or through mechanical means (forced convection).
- Density Differences: Convection is driven by density differences caused by temperature variations in the fluid. Hot fluid expands, becomes less dense, and rises, while cooler fluid sinks.
- Examples: Boiling water in a pot involves convection as the hot water rises and cooler water sinks, creating a circulation pattern. Similarly, the heating and cooling of air in a room involve convection currents.
3. Radiation:
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to transfer heat. The key points about radiation are:
- Electromagnetic Waves: Heat is transferred through the emission and absorption of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation.
- No Medium Required: Unlike conduction and convection, radiation can occur in a vacuum or through transparent mediums, as it does not rely on physical contact or particle movement.
- Examples: The warmth you feel from the sunlight is due to radiation. Similarly, a heated metal object radiates heat to its surroundings.
In summary, conduction involves direct contact between objects, convection requires fluid movement, and radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves. These modes of heat transfer play crucial roles in various natural and technological processes, influencing how heat is distributed and transferred in different systems.
Community Answer
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?
1
Attention Class 7 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 7 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 7.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Similar Class 7 Doubts
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?
Question Description
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?.
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?.
Solutions for what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 7.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ?, a detailed solution for what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? has been provided alongside types of what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is difference between conduction convection and radiation ? tests, examples and also practice Class 7 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























