Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > The reheat factor for steam turbines is defin...
Start Learning for Free
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio of
- a)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy drop
- b)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy drop
- c)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy drop
- d)input velocity to output velocity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulativ...
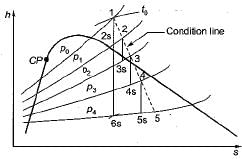
Reheat factor
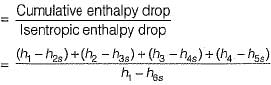
Most Upvoted Answer
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulativ...
Reheat Factor for Steam Turbines
The reheat factor for steam turbines is an important parameter that measures the efficiency of a steam turbine. It is defined as the ratio of the cumulative enthalpy drop to the isentropic enthalpy drop.
Cumulative Enthalpy Drop
The cumulative enthalpy drop is the total amount of energy that is lost by the steam as it passes through the turbine. This energy loss is due to various factors such as friction, heat transfer, and mechanical losses. The cumulative enthalpy drop is calculated by subtracting the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine inlet from the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine outlet.
Isentropic Enthalpy Drop
The isentropic enthalpy drop is the energy loss that would occur if the steam were to expand through the turbine in a perfectly isentropic process. In an isentropic process, the entropy of the steam remains constant. The isentropic enthalpy drop is calculated by subtracting the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine inlet from the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine outlet, assuming that the process is isentropic.
Reheat Factor Calculation
The reheat factor is calculated by dividing the cumulative enthalpy drop by the isentropic enthalpy drop. A higher reheat factor indicates that the turbine is operating more efficiently, as less energy is being lost due to factors such as friction and heat transfer.
Importance of Reheat Factor
The reheat factor is an important parameter for steam turbines as it helps to measure the efficiency of the turbine. A higher reheat factor indicates that the turbine is operating more efficiently, which can result in lower energy costs and higher power generation. By measuring the reheat factor, engineers can identify areas where improvements can be made to increase the efficiency of the turbine.
The reheat factor for steam turbines is an important parameter that measures the efficiency of a steam turbine. It is defined as the ratio of the cumulative enthalpy drop to the isentropic enthalpy drop.
Cumulative Enthalpy Drop
The cumulative enthalpy drop is the total amount of energy that is lost by the steam as it passes through the turbine. This energy loss is due to various factors such as friction, heat transfer, and mechanical losses. The cumulative enthalpy drop is calculated by subtracting the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine inlet from the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine outlet.
Isentropic Enthalpy Drop
The isentropic enthalpy drop is the energy loss that would occur if the steam were to expand through the turbine in a perfectly isentropic process. In an isentropic process, the entropy of the steam remains constant. The isentropic enthalpy drop is calculated by subtracting the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine inlet from the enthalpy of the steam at the turbine outlet, assuming that the process is isentropic.
Reheat Factor Calculation
The reheat factor is calculated by dividing the cumulative enthalpy drop by the isentropic enthalpy drop. A higher reheat factor indicates that the turbine is operating more efficiently, as less energy is being lost due to factors such as friction and heat transfer.
Importance of Reheat Factor
The reheat factor is an important parameter for steam turbines as it helps to measure the efficiency of the turbine. A higher reheat factor indicates that the turbine is operating more efficiently, which can result in lower energy costs and higher power generation. By measuring the reheat factor, engineers can identify areas where improvements can be made to increase the efficiency of the turbine.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The reheat factor for steam turbines is defined as ratio ofa)cumulative enthalpy drop to isentropic enthalpy dropb)isentropic enthalpy drop to cumulative enthalpy dropc)adiabatic enthalpy drop to total enthalpy dropd)input velocity to output velocityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























