Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it....
Start Learning for Free
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?
Most Upvoted Answer
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?
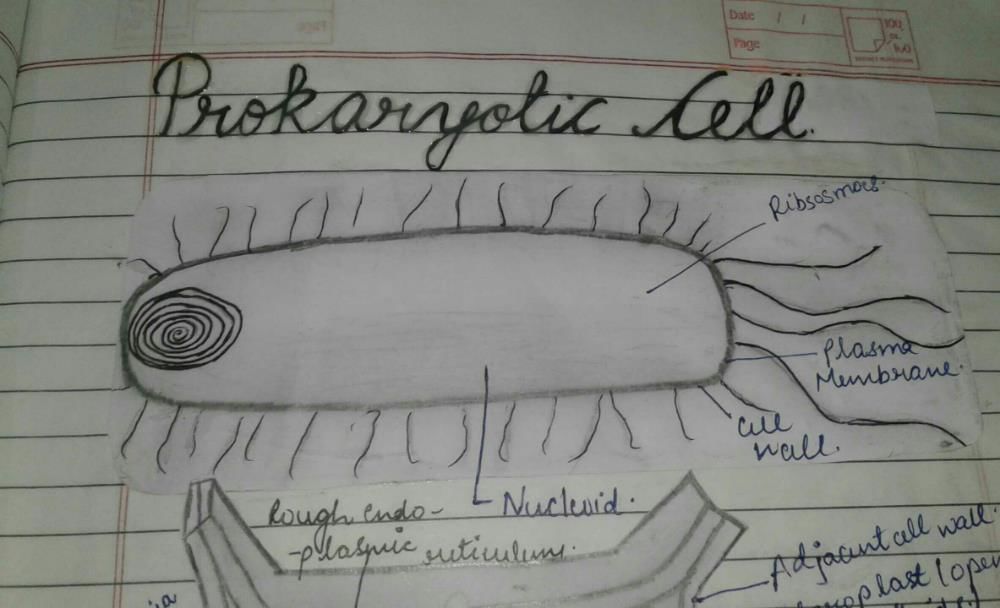
Community Answer
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?
A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Here is a diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell:
_____________________
| |
| Cell Wall |
|_______________________|
| |
| Cell Membrane |
|_______________________|
| |
| Cytoplasm |
|_______________________|
| |
| Nucleoid |
|_______________________|
| |
| Ribosomes |
|_______________________|
| |
| Plasmids |
|_______________________|
| |
| Flagella |
|_______________________|
1. Cell Wall: A rigid outer layer that provides structure and protection to the cell.
2. Cell Membrane: A thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
3. Cytoplasm: A gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains various cellular components.
4. Nucleoid: The region where the genetic material, usually a circular DNA molecule, is located. It is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
5. Ribosomes: Structures responsible for protein synthesis. They are scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
6. Plasmids: Small, circular pieces of DNA that can be found in some prokaryotic cells. They contain additional genetic information and can be transferred between cells.
7. Flagella: Long, whip-like structures that allow the cell to move.
It is important to note that prokaryotic cells can vary in shape and size, so the diagram above represents a generalized prokaryotic cell.
_____________________
| |
| Cell Wall |
|_______________________|
| |
| Cell Membrane |
|_______________________|
| |
| Cytoplasm |
|_______________________|
| |
| Nucleoid |
|_______________________|
| |
| Ribosomes |
|_______________________|
| |
| Plasmids |
|_______________________|
| |
| Flagella |
|_______________________|
1. Cell Wall: A rigid outer layer that provides structure and protection to the cell.
2. Cell Membrane: A thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
3. Cytoplasm: A gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains various cellular components.
4. Nucleoid: The region where the genetic material, usually a circular DNA molecule, is located. It is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
5. Ribosomes: Structures responsible for protein synthesis. They are scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
6. Plasmids: Small, circular pieces of DNA that can be found in some prokaryotic cells. They contain additional genetic information and can be transferred between cells.
7. Flagella: Long, whip-like structures that allow the cell to move.
It is important to note that prokaryotic cells can vary in shape and size, so the diagram above represents a generalized prokaryotic cell.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Question Description
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?.
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?.
Solutions for Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.?, a detailed solution for Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? has been provided alongside types of Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Diagram of Prokaryotic cell & also define it.? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















