Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane...
Start Learning for Free
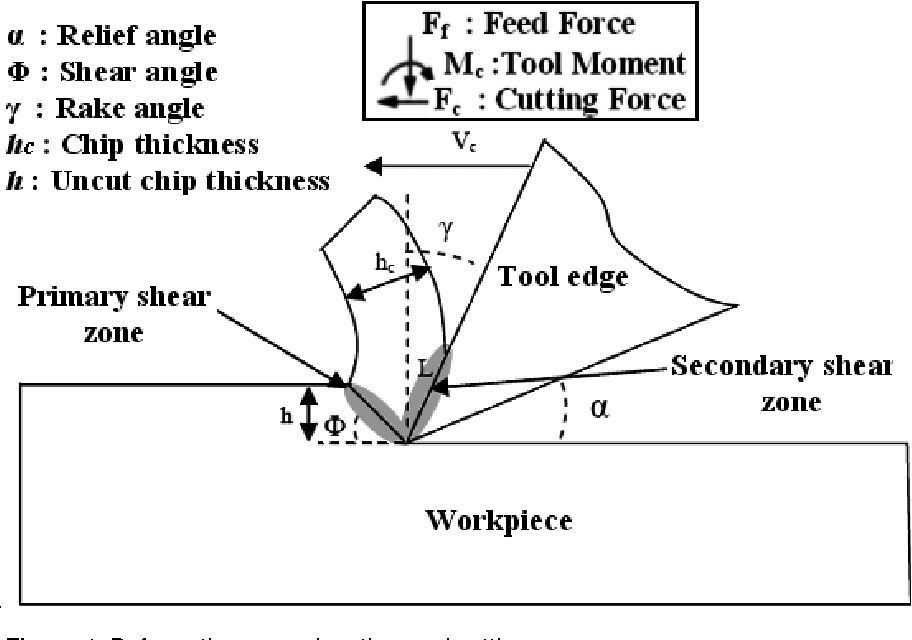
Shear angle is the angle between
- a)shear plane and tool face
- b)shear plane and vertical
- c)shear plane and horizontal
- d)shear plane and job surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear pla...
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear pla...
Explanation:
Shear angle is an important parameter in metal cutting operations. It is defined as the angle between the shear plane and the horizontal plane. The shear plane is the plane along which the shear deformation occurs during metal cutting. The shear angle is determined by various factors such as tool geometry, cutting parameters, material properties, etc.
Shear angle and its significance
The shear angle has a significant impact on the cutting forces, temperature distribution, and surface quality of the machined part. A large shear angle results in high cutting forces and temperatures, which can lead to tool wear and surface roughness. On the other hand, a small shear angle leads to low cutting forces and temperatures but may result in poor surface quality.
Factors affecting shear angle
The shear angle is influenced by various factors, such as tool geometry, cutting speed, feed rate, material properties, etc. The tool geometry, including rake angle, clearance angle, and nose radius, plays a crucial role in determining the shear angle. The cutting speed and feed rate also affect the shear angle, as they determine the amount of material that is removed per unit time. Material properties, such as hardness and ductility, also influence the shear angle.
Importance of job surface
The job surface is the surface of the workpiece that is in contact with the tool during cutting. The orientation of the job surface with respect to the shear plane determines the shear angle. If the job surface is perpendicular to the shear plane, the shear angle will be maximum, resulting in high cutting forces and temperatures. If the job surface is parallel to the shear plane, the shear angle will be minimum, resulting in low cutting forces and temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the shear angle is an important parameter in metal cutting operations. It is determined by various factors, including tool geometry, cutting parameters, and material properties. The orientation of the job surface with respect to the shear plane also plays a crucial role in determining the shear angle. Understanding the shear angle and its significance is essential for achieving optimal cutting performance and surface quality.
Shear angle is an important parameter in metal cutting operations. It is defined as the angle between the shear plane and the horizontal plane. The shear plane is the plane along which the shear deformation occurs during metal cutting. The shear angle is determined by various factors such as tool geometry, cutting parameters, material properties, etc.
Shear angle and its significance
The shear angle has a significant impact on the cutting forces, temperature distribution, and surface quality of the machined part. A large shear angle results in high cutting forces and temperatures, which can lead to tool wear and surface roughness. On the other hand, a small shear angle leads to low cutting forces and temperatures but may result in poor surface quality.
Factors affecting shear angle
The shear angle is influenced by various factors, such as tool geometry, cutting speed, feed rate, material properties, etc. The tool geometry, including rake angle, clearance angle, and nose radius, plays a crucial role in determining the shear angle. The cutting speed and feed rate also affect the shear angle, as they determine the amount of material that is removed per unit time. Material properties, such as hardness and ductility, also influence the shear angle.
Importance of job surface
The job surface is the surface of the workpiece that is in contact with the tool during cutting. The orientation of the job surface with respect to the shear plane determines the shear angle. If the job surface is perpendicular to the shear plane, the shear angle will be maximum, resulting in high cutting forces and temperatures. If the job surface is parallel to the shear plane, the shear angle will be minimum, resulting in low cutting forces and temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the shear angle is an important parameter in metal cutting operations. It is determined by various factors, including tool geometry, cutting parameters, and material properties. The orientation of the job surface with respect to the shear plane also plays a crucial role in determining the shear angle. Understanding the shear angle and its significance is essential for achieving optimal cutting performance and surface quality.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Shear angle is the angle betweena)shear plane and tool faceb)shear plane and verticalc)shear plane and horizontald)shear plane and job surfaceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















