Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > A circular cylinder partly filled with a liq...
Start Learning for Free
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will be
- a)ω2r2 / g
- b)ω2r2 / 2g
- c)ω2r2 / 4g
- d)ω2r2 / 8g
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its ...
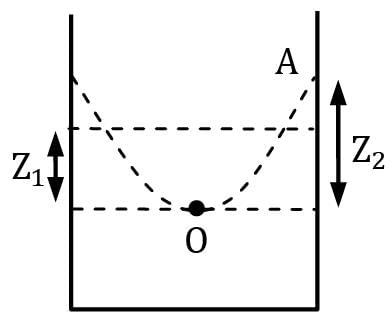
Volume of parallelepiped
=1 / 2× πr2Z2 = πr2Z1
Z2 = 2Z1
Taking 0 as origin at gauge pressure
p = ρω2r2 / 2 − ρg Z + C
atO,p = 0,r = 0,Z = 0so,C = 0
at A p = 0 = ρω2r2 / 2 − lgZ1 ⟹ Z2 = ω2r2 / 2g
he rise of liquid above original level (Z1)
= Z2 − Z1 ⟹ Z2 − Z2 / 2 = Z2 / 2 = ω2r2 / 4g
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its ...
The rise of the liquid surface in a rotating cylinder can be explained by the centrifugal force acting on the liquid. When a liquid is rotated in a cylindrical container, it experiences an outward force due to its inertia. This force is known as the centrifugal force.
To determine the rise of the liquid surface, we need to consider the balance between the centrifugal force and the gravitational force acting on the liquid. The gravitational force acts vertically downward, while the centrifugal force acts radially outward.
Let's consider a small element of liquid at a distance r from the axis of rotation. The centrifugal force acting on this element can be calculated using the formula:
Fc = ρω^2r
Where ρ is the density of the liquid and ω is the angular velocity of rotation.
The gravitational force acting on the element can be calculated using the formula:
Fg = ρgV
Where g is the acceleration due to gravity and V is the volume of the element.
The rise of the liquid surface can be determined by equating these two forces:
Fc = Fg
ρω^2r = ρgV
Since the element is in the shape of a circular disk, its volume can be calculated using the formula:
V = πr^2h
Where h is the rise of the liquid surface.
Substituting this into the equation, we get:
ρω^2r = ρgπr^2h
Simplifying the equation, we find:
h = ω^2r / (gπ)
Now, let's compare this with the given options:
a) ω^2r^2 / g
b) ω^2r^2 / (2g)
c) ω^2r^2 / (4g)
d) ω^2r^2 / (8g)
We can see that the correct answer is option C, as the rise of the liquid surface is given by ω^2r^2 / (4g).
Therefore, the rise of the liquid surface above the original level in a rotating cylinder is ω^2r^2 / (4g).
To determine the rise of the liquid surface, we need to consider the balance between the centrifugal force and the gravitational force acting on the liquid. The gravitational force acts vertically downward, while the centrifugal force acts radially outward.
Let's consider a small element of liquid at a distance r from the axis of rotation. The centrifugal force acting on this element can be calculated using the formula:
Fc = ρω^2r
Where ρ is the density of the liquid and ω is the angular velocity of rotation.
The gravitational force acting on the element can be calculated using the formula:
Fg = ρgV
Where g is the acceleration due to gravity and V is the volume of the element.
The rise of the liquid surface can be determined by equating these two forces:
Fc = Fg
ρω^2r = ρgV
Since the element is in the shape of a circular disk, its volume can be calculated using the formula:
V = πr^2h
Where h is the rise of the liquid surface.
Substituting this into the equation, we get:
ρω^2r = ρgπr^2h
Simplifying the equation, we find:
h = ω^2r / (gπ)
Now, let's compare this with the given options:
a) ω^2r^2 / g
b) ω^2r^2 / (2g)
c) ω^2r^2 / (4g)
d) ω^2r^2 / (8g)
We can see that the correct answer is option C, as the rise of the liquid surface is given by ω^2r^2 / (4g).
Therefore, the rise of the liquid surface above the original level in a rotating cylinder is ω^2r^2 / (4g).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A circular cylinder partly filled with a liquid is rotated about its axis at ω rad/s without spilling. At the walls, the rise of liquid surface above the original level will bea) ω2r2 / gb) ω2r2 / 2gc) ω2r2 / 4gd) ω2r2 / 8gCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























