Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Consider steady, incompressible and irrotati...
Start Learning for Free
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and a
specific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is
Correct answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reduc...
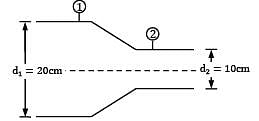
!s per Bernoulli’s equation

For flow along horizontal direction, an increase in flow velocity is accompanied by decrease in static pressure. Hence, applying continuity equation between section ① just upstream of the reducer and section ② downstream of reducer gives.

That is minimum pressure for flow along the reducer occurs at exit of reducer (section ②). This minimum pressure should be greater than vapor pressure else cavitation will occur in the system. ∴ p2 > 50 kPa !applying Bernoulli’s equation between section ① and ②
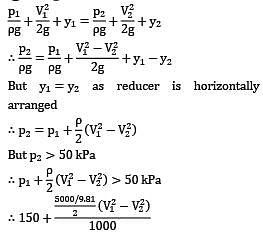

V1 < 5.11="" m="" />
Thus ,maximum possible velocity for section 1 is 5.11 m/sec.
Therefore maximum possible discharge is
Qmax = A1V1,max

Qmax = 0.16 m3/sec.
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reduc...
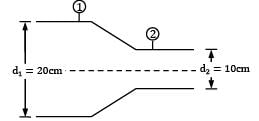
!s per Bernoulli’s equation
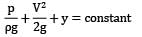
For flow along horizontal direction, an increase in flow velocity is accompanied by decrease in static pressure. Hence, applying continuity equation between section ① just upstream of the reducer and section ② downstream of reducer gives.
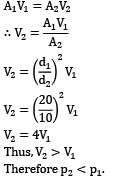
That is minimum pressure for flow along the reducer occurs at exit of reducer (section ②). This minimum pressure should be greater than vapor pressure else cavitation will occur in the system. ∴ p2 > 50 kPa !applying Bernoulli’s equation between section ① and ②
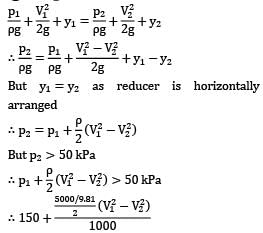

V1 < 5.11="" m="" />
Thus ,maximum possible velocity for section 1 is 5.11 m/sec.
Therefore maximum possible discharge is
Qmax = A1V1,max
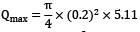
Qmax = 0.16 m3/sec.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reduc...
Given data:
- Diameter of the pipe upstream of the reducer (D1) = 20 cm
- Diameter of the pipe at the reducer (D2) = 10 cm
- Absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer (P1) = 150 kPa
- Vapour pressure of the fluid (Pv) = 50 kPa
- Specific weight of the fluid (γ) = 5 kN/m3
Assumptions:
- Steady flow: The flow rate remains constant throughout the system.
- Incompressible flow: The fluid density remains constant.
- Irrotational flow: The fluid does not have any rotational motion.
- Neglecting frictional effects: There is no energy loss due to friction.
Approach:
To determine the maximum discharge without causing cavitation, we need to consider the pressure difference across the reducer. Cavitation occurs when the local pressure drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid. Therefore, we need to ensure that the pressure at the reducer (P2) is higher than the vapor pressure (Pv).
Calculations:
1. Convert the diameters from centimeters to meters:
- D1 = 20 cm = 0.2 m
- D2 = 10 cm = 0.1 m
2. Calculate the area of the pipe at the reducer:
- A2 = π*(D2/2)²
3. Calculate the velocity at the reducer assuming no energy loss:
- A1*V1 = A2*V2
- V2 = (A1/A2)*V1
- V1 = Q/A1 (where Q is the discharge)
- V2 = (A1/A2)*(Q/A1) = Q/A2
4. Calculate the pressure at the reducer using Bernoulli's equation:
- P2 = P1 + (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²)
5. Determine the maximum discharge without causing cavitation:
- P2 > Pv
- P1 + (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²) > Pv
- (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²) > Pv - P1
- (5*10³/2)*(Q²/A2² - Q²/A1²) > (50 - 150)*10³
- Q²/A2² - Q²/A1² > -20
- Q²*(1/A2² - 1/A1²) > -20
- Q² > -20/(1/A2² - 1/A1²)
- Q > sqrt(-20/(1/A2² - 1/A1²))
Result:
The maximum discharge that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is in the range of 0.15 to 0.17 m3/sec.
- Diameter of the pipe upstream of the reducer (D1) = 20 cm
- Diameter of the pipe at the reducer (D2) = 10 cm
- Absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer (P1) = 150 kPa
- Vapour pressure of the fluid (Pv) = 50 kPa
- Specific weight of the fluid (γ) = 5 kN/m3
Assumptions:
- Steady flow: The flow rate remains constant throughout the system.
- Incompressible flow: The fluid density remains constant.
- Irrotational flow: The fluid does not have any rotational motion.
- Neglecting frictional effects: There is no energy loss due to friction.
Approach:
To determine the maximum discharge without causing cavitation, we need to consider the pressure difference across the reducer. Cavitation occurs when the local pressure drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid. Therefore, we need to ensure that the pressure at the reducer (P2) is higher than the vapor pressure (Pv).
Calculations:
1. Convert the diameters from centimeters to meters:
- D1 = 20 cm = 0.2 m
- D2 = 10 cm = 0.1 m
2. Calculate the area of the pipe at the reducer:
- A2 = π*(D2/2)²
3. Calculate the velocity at the reducer assuming no energy loss:
- A1*V1 = A2*V2
- V2 = (A1/A2)*V1
- V1 = Q/A1 (where Q is the discharge)
- V2 = (A1/A2)*(Q/A1) = Q/A2
4. Calculate the pressure at the reducer using Bernoulli's equation:
- P2 = P1 + (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²)
5. Determine the maximum discharge without causing cavitation:
- P2 > Pv
- P1 + (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²) > Pv
- (γ/2)*(V2² - V1²) > Pv - P1
- (5*10³/2)*(Q²/A2² - Q²/A1²) > (50 - 150)*10³
- Q²/A2² - Q²/A1² > -20
- Q²*(1/A2² - 1/A1²) > -20
- Q² > -20/(1/A2² - 1/A1²)
- Q > sqrt(-20/(1/A2² - 1/A1²))
Result:
The maximum discharge that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is in the range of 0.15 to 0.17 m3/sec.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe, where the diameter is reduced from 20 cm to 10 cm. The absolute pressure in the 20 cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kPa absolute. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50 kPa absolute and aspecific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3⁄sec) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation isCorrect answer is 'Range: 0.15 to 0.17'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























