SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h...
Start Learning for Free
The steady flow energy equation:
Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:
- a)Nozzle
- b)Turbine
- c)Compressor
- d)Boiler
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)No...
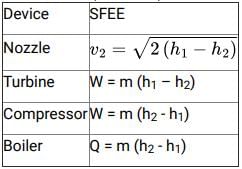
From Steady Flow Energy Equation (S.F.E.E.)
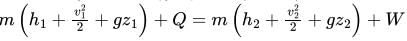
For Boiler: W=0, no work is done by the boiler,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected.
i.e. Q=m(h2−h1)
For Nozzle: Q=0, as the nozzle is perfectly insulated,
W=0, no work is done by nozzle, \(v_{1}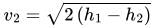
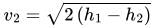
For Turbine: Q=0, for the adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W=m(h1−h2)
for Compressor: Q=0, for an adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W = m (h2 − h1)
Most Upvoted Answer
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)No...
From Steady Flow Energy Equation (S.F.E.E.)
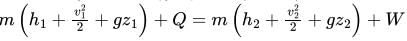
For Boiler: W=0, no work is done by the boiler,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected.
i.e. Q=m(h2−h1)
For Nozzle: Q=0, as the nozzle is perfectly insulated,
W=0, no work is done by nozzle, \(v_{1}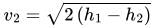
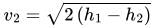
For Turbine: Q=0, for the adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W=m(h1−h2)
for Compressor: Q=0, for an adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W = m (h2 − h1)

Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)No...
Steady Flow Energy Equation
The steady flow energy equation, also known as the first law of thermodynamics for steady flow processes, is a fundamental equation used in thermodynamics. It relates the heat transfer, work done, and changes in enthalpy of a fluid flowing through a system. The equation is given by:
Q = m(h2 – h1)
Where:
- Q is the heat transfer
- m is the mass flow rate of the fluid
- h2 is the enthalpy at the outlet of the system
- h1 is the enthalpy at the inlet of the system
Applicability of the Equation
The steady flow energy equation is applicable for various devices and processes in thermodynamics. However, in this case, the correct answer is option 'D', which is the boiler. Let's see why the equation is applicable to a boiler:
Boiler
A boiler is a device used to convert water into steam by the application of heat. It is commonly used in power plants, industrial processes, and heating systems. In a boiler, fuel is burned to produce heat, which is transferred to the water to generate steam.
- Heat Transfer: In a boiler, heat is transferred from the burning fuel to the water through various mechanisms such as radiation, convection, and conduction. This heat transfer is represented as Q in the steady flow energy equation.
- Mass Flow Rate: The mass flow rate of the fluid, in this case, is the rate at which water is converted into steam. It is denoted by m in the equation.
- Enthalpy: The enthalpy of the fluid at the inlet and outlet of the boiler is represented by h1 and h2, respectively. The enthalpy change is a result of the heat transfer and phase change of the water to steam.
By applying the steady flow energy equation to a boiler, we can calculate the heat transfer (Q) based on the mass flow rate (m) and the enthalpy change (h2 – h1). This equation allows us to analyze and calculate the energy balance in a boiler system.
Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer as the steady flow energy equation is applicable to a boiler.
The steady flow energy equation, also known as the first law of thermodynamics for steady flow processes, is a fundamental equation used in thermodynamics. It relates the heat transfer, work done, and changes in enthalpy of a fluid flowing through a system. The equation is given by:
Q = m(h2 – h1)
Where:
- Q is the heat transfer
- m is the mass flow rate of the fluid
- h2 is the enthalpy at the outlet of the system
- h1 is the enthalpy at the inlet of the system
Applicability of the Equation
The steady flow energy equation is applicable for various devices and processes in thermodynamics. However, in this case, the correct answer is option 'D', which is the boiler. Let's see why the equation is applicable to a boiler:
Boiler
A boiler is a device used to convert water into steam by the application of heat. It is commonly used in power plants, industrial processes, and heating systems. In a boiler, fuel is burned to produce heat, which is transferred to the water to generate steam.
- Heat Transfer: In a boiler, heat is transferred from the burning fuel to the water through various mechanisms such as radiation, convection, and conduction. This heat transfer is represented as Q in the steady flow energy equation.
- Mass Flow Rate: The mass flow rate of the fluid, in this case, is the rate at which water is converted into steam. It is denoted by m in the equation.
- Enthalpy: The enthalpy of the fluid at the inlet and outlet of the boiler is represented by h1 and h2, respectively. The enthalpy change is a result of the heat transfer and phase change of the water to steam.
By applying the steady flow energy equation to a boiler, we can calculate the heat transfer (Q) based on the mass flow rate (m) and the enthalpy change (h2 – h1). This equation allows us to analyze and calculate the energy balance in a boiler system.
Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer as the steady flow energy equation is applicable to a boiler.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Question Description
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:a)Nozzleb)Turbinec)Compressord)BoilerCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























