Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Read the passage given below and answer the f...
Start Learning for Free
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.
A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.
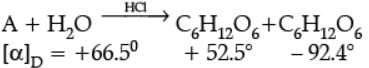
The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.
A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.
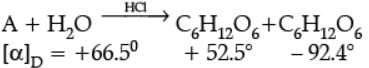
- a)C-1 is anomeric carbon
- b)C-5 is anomeric carbon
- c)3’-OH groups are present
- d)5’-OH groups are present
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The tw...
It indicates that 5’-OH groups are present which react with acetic acid to give glucose pentaacetate.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Question Description
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The two monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e., aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars, e.g., sucrose. On the other hand, sugars in which these functional groups are free, are called reducing sugars, for example, maltose and lactose.A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)– glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.a)C-1 is anomeric carbonb)C-5 is anomeric carbonc)3’-OH groups are presentd)5’-OH groups are presentCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















