Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Questions > fundamental rights Related: Short and Long A...
Start Learning for Free
fundamental rights
?Most Upvoted Answer
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Const...
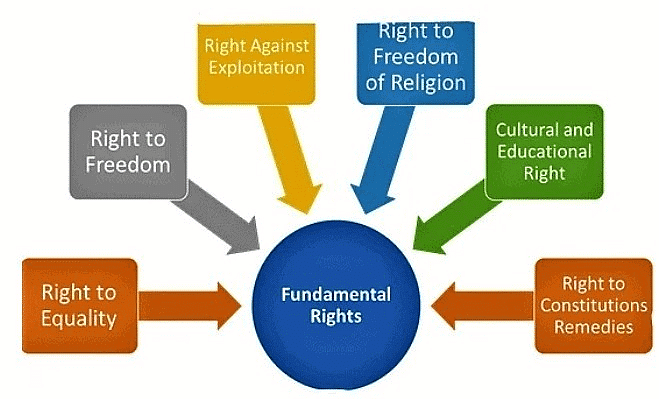
Community Answer
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Const...
Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution
Fundamental rights are a set of basic rights and freedoms that are guaranteed to all citizens of India. These rights are enshrined in Part III of the Indian Constitution and are considered to be the cornerstone of Indian democracy. The Constitution provides individuals with certain rights that are essential for their overall development and well-being.
Key Features of Fundamental Rights:
1. Justiciable: Fundamental rights are legally enforceable, which means that individuals can approach the courts in case of any violation.
2. Universal: These rights are available to all citizens of India, irrespective of their caste, religion, gender, or place of birth.
3. Equality: Fundamental rights ensure equality before the law and prohibit discrimination on various grounds.
4. Individual Rights: These rights are granted to individuals and not to the community or group as a whole.
Types of Fundamental Rights:
1. Right to Equality: This includes the right to equality before law, prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth, and equality of opportunity in matters of employment.
2. Right to Freedom: This includes the freedom of speech and expression, assembly, association, movement, residence, and profession.
3. Right against Exploitation: This includes the prohibition of forced labor, child labor, and trafficking of human beings.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion: This guarantees individuals the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate any religion of their choice.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights: This includes the right to preserve one's culture, language, and script. It also ensures the right to education for all children aged 6-14 years.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies: This enables individuals to seek legal remedies for the violation of their fundamental rights. It includes the right to move the Supreme Court or High Courts for the enforcement of these rights.
Importance of Fundamental Rights:
1. Protection of Individual Liberty: Fundamental rights safeguard the individual liberty and dignity of citizens by ensuring their basic freedoms.
2. Equality and Social Justice: These rights promote equality and social justice by prohibiting discrimination and ensuring equal opportunities.
3. Protection against State Tyranny: Fundamental rights act as a check on the arbitrary exercise of power by the state and protect individuals from state oppression.
4. Empowerment of Citizens: By guaranteeing certain rights, the Constitution empowers citizens to actively participate in the democratic process.
In conclusion, fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution are a crucial aspect of ensuring individual liberty, equality, and social justice. These rights play a vital role in upholding the democratic principles on which India's governance system is based.
Fundamental rights are a set of basic rights and freedoms that are guaranteed to all citizens of India. These rights are enshrined in Part III of the Indian Constitution and are considered to be the cornerstone of Indian democracy. The Constitution provides individuals with certain rights that are essential for their overall development and well-being.
Key Features of Fundamental Rights:
1. Justiciable: Fundamental rights are legally enforceable, which means that individuals can approach the courts in case of any violation.
2. Universal: These rights are available to all citizens of India, irrespective of their caste, religion, gender, or place of birth.
3. Equality: Fundamental rights ensure equality before the law and prohibit discrimination on various grounds.
4. Individual Rights: These rights are granted to individuals and not to the community or group as a whole.
Types of Fundamental Rights:
1. Right to Equality: This includes the right to equality before law, prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth, and equality of opportunity in matters of employment.
2. Right to Freedom: This includes the freedom of speech and expression, assembly, association, movement, residence, and profession.
3. Right against Exploitation: This includes the prohibition of forced labor, child labor, and trafficking of human beings.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion: This guarantees individuals the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate any religion of their choice.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights: This includes the right to preserve one's culture, language, and script. It also ensures the right to education for all children aged 6-14 years.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies: This enables individuals to seek legal remedies for the violation of their fundamental rights. It includes the right to move the Supreme Court or High Courts for the enforcement of these rights.
Importance of Fundamental Rights:
1. Protection of Individual Liberty: Fundamental rights safeguard the individual liberty and dignity of citizens by ensuring their basic freedoms.
2. Equality and Social Justice: These rights promote equality and social justice by prohibiting discrimination and ensuring equal opportunities.
3. Protection against State Tyranny: Fundamental rights act as a check on the arbitrary exercise of power by the state and protect individuals from state oppression.
4. Empowerment of Citizens: By guaranteeing certain rights, the Constitution empowers citizens to actively participate in the democratic process.
In conclusion, fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution are a crucial aspect of ensuring individual liberty, equality, and social justice. These rights play a vital role in upholding the democratic principles on which India's governance system is based.
Attention Class 8 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 8 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 8.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Similar Class 8 Doubts
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution?
Question Description
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution?.
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution?.
Solutions for fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 8.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution?, a detailed solution for fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? has been provided alongside types of fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice fundamental rights Related: Short and Long Answers - The Indian Constitution? tests, examples and also practice Class 8 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























