Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts...
Start Learning for Free
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as a
- a)2 Terminal unidirectional switch
- b)2 Terminal bidirectional switch
- c)3 Terminal bidirectional switch
- d)5 terminal multi-directional switch
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidire...
Triac as a 3 Terminal Bidirectional Switch
A triac is a semiconductor device that acts as a bidirectional switch and is commonly used in AC power control applications. It is a three-terminal device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered appropriately. The correct answer to the given question is option 'C', which states that a triac is a three-terminal bidirectional switch.
Three-Terminal Device
A triac consists of three terminals: Main Terminal 1 (MT1), Main Terminal 2 (MT2), and Gate (G). These terminals are used to control the flow of current through the device.
Bidirectional Switch
A bidirectional switch is a device that can control the flow of current in both directions. Unlike a unidirectional switch, which can only conduct current in one direction, a bidirectional switch is suitable for AC power control applications where the current periodically changes direction.
Working Principle
A triac is a two-way thyristor, meaning it can conduct current in both directions. It consists of two SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) structures connected in parallel but in opposite directions. The operation of a triac can be understood by considering the four quadrants of its operation.
1. Quadrant I: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is positive, and the gate current is positive. The triac is forward-biased, and it conducts current. This quadrant represents the positive half-cycle of an AC waveform.
2. Quadrant II: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is negative, and the gate current is positive. The triac is reverse-biased, and it does not conduct current. This quadrant represents the negative half-cycle of an AC waveform.
3. Quadrant III: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is negative, and the gate current is negative. The triac is forward-biased, and it conducts current. This quadrant represents the negative half-cycle of an AC waveform.
4. Quadrant IV: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is positive, and the gate current is negative. The triac is reverse-biased, and it does not conduct current. This quadrant represents the positive half-cycle of an AC waveform.
Applications
Due to its bidirectional switching capability, a triac is widely used in various AC power control applications such as:
1. Dimmer switches: Triacs are commonly used in lighting control circuits to adjust the brightness of incandescent lamps.
2. Motor speed control: Triacs can be used to control the speed of AC motors.
3. Heating control: Triacs are used in electric heaters and ovens for temperature control.
4. Power control: Triacs are used for power regulation in AC circuits.
In conclusion, a triac is a three-terminal bidirectional switch that can conduct current in both directions when triggered appropriately. It is a versatile device widely used in AC power control applications.
A triac is a semiconductor device that acts as a bidirectional switch and is commonly used in AC power control applications. It is a three-terminal device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered appropriately. The correct answer to the given question is option 'C', which states that a triac is a three-terminal bidirectional switch.
Three-Terminal Device
A triac consists of three terminals: Main Terminal 1 (MT1), Main Terminal 2 (MT2), and Gate (G). These terminals are used to control the flow of current through the device.
Bidirectional Switch
A bidirectional switch is a device that can control the flow of current in both directions. Unlike a unidirectional switch, which can only conduct current in one direction, a bidirectional switch is suitable for AC power control applications where the current periodically changes direction.
Working Principle
A triac is a two-way thyristor, meaning it can conduct current in both directions. It consists of two SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) structures connected in parallel but in opposite directions. The operation of a triac can be understood by considering the four quadrants of its operation.
1. Quadrant I: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is positive, and the gate current is positive. The triac is forward-biased, and it conducts current. This quadrant represents the positive half-cycle of an AC waveform.
2. Quadrant II: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is negative, and the gate current is positive. The triac is reverse-biased, and it does not conduct current. This quadrant represents the negative half-cycle of an AC waveform.
3. Quadrant III: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is negative, and the gate current is negative. The triac is forward-biased, and it conducts current. This quadrant represents the negative half-cycle of an AC waveform.
4. Quadrant IV: In this quadrant, the voltage across MT1 and MT2 is positive, and the gate current is negative. The triac is reverse-biased, and it does not conduct current. This quadrant represents the positive half-cycle of an AC waveform.
Applications
Due to its bidirectional switching capability, a triac is widely used in various AC power control applications such as:
1. Dimmer switches: Triacs are commonly used in lighting control circuits to adjust the brightness of incandescent lamps.
2. Motor speed control: Triacs can be used to control the speed of AC motors.
3. Heating control: Triacs are used in electric heaters and ovens for temperature control.
4. Power control: Triacs are used for power regulation in AC circuits.
In conclusion, a triac is a three-terminal bidirectional switch that can conduct current in both directions when triggered appropriately. It is a versatile device widely used in AC power control applications.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidire...
Triac:
- A Triac is a bidirectional thyristor with three terminals i.e. it can conduct in both directions.
- Its three terminals are usually designated as MT1 (Anode 1), MT2 (Anode 2), and the gate by G as in a thyristor.
- When in operation, a Triac is equivalent to two SCRs connected in antiparallel.
- As the Triac can conduct in both directions, the terms anode and cathode are not applicable to Triac.
- It is used extensively for the control of power in ac circuits.
The symbol and the i-v characteristics of triac are shown below.
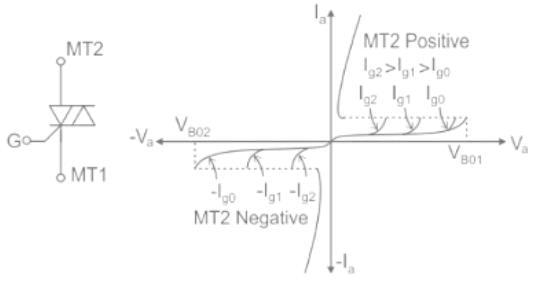
A triac may sometimes operate in the rectifier mode rather than in the bidirectional mode. This may happen due to the following reasons.

A triac may sometimes operate in the rectifier mode rather than in the bidirectional mode. This may happen due to the following reasons.
- For a given value of positive gate current, a triac may turn on with MT2 positive in the first quadrant but may fail to turn on with MT2 negative.
- With constant negative gate current, the triac may turn on with MT2 negative in the third quadrant but may not turn on with MT2 positive.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A triac is a semi-conductor device which acts as aa)2 Terminal unidirectional switchb)2 Terminal bidirectional switchc)3 Terminal bidirectional switchd)5 terminal multi-directional switchCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















