Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 1...
Start Learning for Free
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.
- a)0.1
- b)0.4
- c)0.8
- d)1.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of t...
CONCEPT:
The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
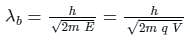
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
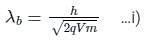
For cut off wavele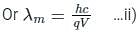 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have
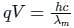
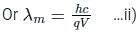
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
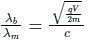
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is
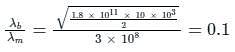
The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
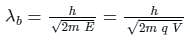
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
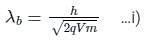
For cut off wavele
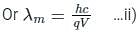 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have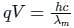
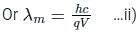
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
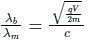
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is
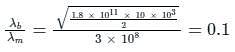
Most Upvoted Answer
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of t...
CONCEPT:
The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
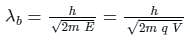
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
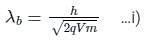
For cut off wavele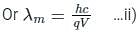 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have
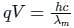
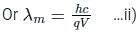
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
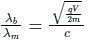
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is
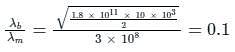
The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
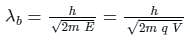
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
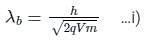
For cut off wavele
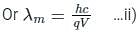 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have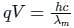
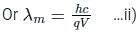
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
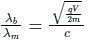
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is
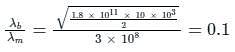
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of t...
To find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced, we need to use the equation for the de-Broglie wavelength:
λ = h / (mv)
Where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s), m is the mass of the electron, and v is the velocity of the electron.
The specific charge of an electron is given by the equation:
q/m = specific charge
Where q is the charge of the electron (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) and m is the mass of the electron.
Given that the specific charge of an electron is 1.8 x 10^11 C/kg, we can solve for the mass of the electron:
(1.8 x 10^11 C/kg) = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) / m
m = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) / (1.8 x 10^11 C/kg)
m ≈ -8.89 x 10^-31 kg
Now, we can calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons:
λ = (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s) / ((-8.89 x 10^-31 kg) * v)
To find the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced, we can use the equation:
λ = c / f
Where λ is the wavelength, c is the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s), and f is the frequency of the X-rays.
The voltage of the X-ray tube is given as 10 kV, which is equal to 10,000 V. We can use this voltage to find the frequency of the X-rays:
f = (q * V) / h
f = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C * 10,000 V) / (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s)
Now we can calculate the shortest wavelength of the X-rays:
λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / ((-1.6 x 10^-19 C * 10,000 V) / (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s))
Finally, we can find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength to the shortest wavelength by dividing the two values:
Ratio = (de-Broglie wavelength) / (shortest wavelength)
λ = h / (mv)
Where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s), m is the mass of the electron, and v is the velocity of the electron.
The specific charge of an electron is given by the equation:
q/m = specific charge
Where q is the charge of the electron (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) and m is the mass of the electron.
Given that the specific charge of an electron is 1.8 x 10^11 C/kg, we can solve for the mass of the electron:
(1.8 x 10^11 C/kg) = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) / m
m = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C) / (1.8 x 10^11 C/kg)
m ≈ -8.89 x 10^-31 kg
Now, we can calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons:
λ = (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s) / ((-8.89 x 10^-31 kg) * v)
To find the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced, we can use the equation:
λ = c / f
Where λ is the wavelength, c is the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s), and f is the frequency of the X-rays.
The voltage of the X-ray tube is given as 10 kV, which is equal to 10,000 V. We can use this voltage to find the frequency of the X-rays:
f = (q * V) / h
f = (-1.6 x 10^-19 C * 10,000 V) / (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s)
Now we can calculate the shortest wavelength of the X-rays:
λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / ((-1.6 x 10^-19 C * 10,000 V) / (6.626 x 10^-34 J.s))
Finally, we can find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength to the shortest wavelength by dividing the two values:
Ratio = (de-Broglie wavelength) / (shortest wavelength)

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.a)0.1b)0.4c)0.8d)1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















