Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > What is the power dissipation (in W) in an id...
Start Learning for Free
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?
- a)-0.04
- b)-0.2 1
- c)0
- d)0.04
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an in...
AC through Pure Inductor:
Consider a pure inductor of inductance L connected to an alternating voltage given by,
v = Vm sin ωt
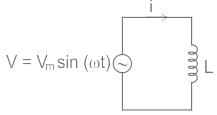
An alternating current (i) flows through the inductor and sets up a changing magnetic field and it induced a back EMF (-L di/dt).
By using KVL,
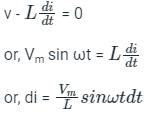
Integrating on both side,
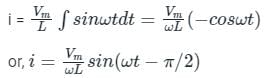
The phasor diagram can be drawn as,
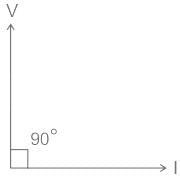
From the phasor diagram, it is clear that the phase angle between voltage and current is 90°.
We know that the power factor is the cosine angle of voltage and current,
Hence, Power Factor = cos ϕ = cos 90° = 0
We know that,
Power Dissipation (P) = VIcos ϕ
Since, ϕ = 90° ⇒ cos ϕ = cos 90° = 0
Hence, Power Dissipation (P) = 0
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an in...
Power Dissipation in an Ideal Inductor
In an ideal inductor, the power dissipation is zero. This is because an ideal inductor has zero resistance and therefore does not dissipate any power in the form of heat.
Explanation:
Inductors are passive electrical components that store energy in their magnetic field. When a current flows through an inductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. The energy stored in this magnetic field is given by the equation:
E = 0.5 * L * I^2
Where:
E is the energy stored in the inductor (in joules),
L is the inductance of the inductor (in henries), and
I is the current flowing through the inductor (in amperes).
Since power is the rate at which energy is transferred, the power dissipated by an inductor can be calculated by differentiating the energy with respect to time:
P = dE/dt
However, in the case of an ideal inductor, the inductor has no resistance, which means that there is no power dissipated as heat. In other words, an ideal inductor does not convert electrical energy into heat energy.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the power dissipation in an ideal inductor is zero (0 W). This is because an ideal inductor has zero resistance and does not dissipate any power in the form of heat.
In an ideal inductor, the power dissipation is zero. This is because an ideal inductor has zero resistance and therefore does not dissipate any power in the form of heat.
Explanation:
Inductors are passive electrical components that store energy in their magnetic field. When a current flows through an inductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. The energy stored in this magnetic field is given by the equation:
E = 0.5 * L * I^2
Where:
E is the energy stored in the inductor (in joules),
L is the inductance of the inductor (in henries), and
I is the current flowing through the inductor (in amperes).
Since power is the rate at which energy is transferred, the power dissipated by an inductor can be calculated by differentiating the energy with respect to time:
P = dE/dt
However, in the case of an ideal inductor, the inductor has no resistance, which means that there is no power dissipated as heat. In other words, an ideal inductor does not convert electrical energy into heat energy.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the power dissipation in an ideal inductor is zero (0 W). This is because an ideal inductor has zero resistance and does not dissipate any power in the form of heat.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the power dissipation (in W) in an ideal inductor having an inductance of 0.2 H?a)-0.04b)-0.2 1c)0d)0.04Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















