GATE Exam > GATE Questions > A signal channel signal acquisition system wi...
Start Learning for Free
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC is
- a)49 ms
- b)0.49 ms
- c)4.9 ms
- d)490 ms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist o...
V/s. The system is connected to a 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with a conversion time of 10 μs. The clock frequency of the ADC is 1 MHz.
To calculate the maximum allowable drop in voltage during the conversion time, we need to consider the worst case drop rate of the sample and hold circuit and the conversion time of the ADC.
The maximum allowable drop in voltage can be calculated using the formula:
Maximum Allowable Drop = Drop Rate * Conversion Time
Given that the drop rate is 100 V/s and the conversion time is 10 μs (or 10^-5 s), we can plug in these values into the formula:
Maximum Allowable Drop = 100 V/s * 10^-5 s
= 1 V
Therefore, the maximum allowable drop in voltage during the conversion time is 1 V.
Now, let's consider the clock frequency of the ADC, which is 1 MHz. This means that the ADC performs 1 million conversions per second.
Since the ADC has a 12-bit resolution, it can represent 2^12 = 4096 different voltage levels. Therefore, the voltage resolution of the ADC can be calculated as:
Voltage Resolution = (Voltage Range) / (Number of Levels)
= (10 V) / (4096)
≈ 0.00244 V
Therefore, the voltage resolution of the ADC is approximately 0.00244 V.
In summary, the signal acquisition system with a 0-10 V range can tolerate a maximum allowable drop in voltage of 1 V during the conversion time of the ADC. The ADC has a voltage resolution of approximately 0.00244 V.
To calculate the maximum allowable drop in voltage during the conversion time, we need to consider the worst case drop rate of the sample and hold circuit and the conversion time of the ADC.
The maximum allowable drop in voltage can be calculated using the formula:
Maximum Allowable Drop = Drop Rate * Conversion Time
Given that the drop rate is 100 V/s and the conversion time is 10 μs (or 10^-5 s), we can plug in these values into the formula:
Maximum Allowable Drop = 100 V/s * 10^-5 s
= 1 V
Therefore, the maximum allowable drop in voltage during the conversion time is 1 V.
Now, let's consider the clock frequency of the ADC, which is 1 MHz. This means that the ADC performs 1 million conversions per second.
Since the ADC has a 12-bit resolution, it can represent 2^12 = 4096 different voltage levels. Therefore, the voltage resolution of the ADC can be calculated as:
Voltage Resolution = (Voltage Range) / (Number of Levels)
= (10 V) / (4096)
≈ 0.00244 V
Therefore, the voltage resolution of the ADC is approximately 0.00244 V.
In summary, the signal acquisition system with a 0-10 V range can tolerate a maximum allowable drop in voltage of 1 V during the conversion time of the ADC. The ADC has a voltage resolution of approximately 0.00244 V.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist o...
In an ADC along with sample and hold circuit, for avoiding error at the output, the voltage of the capacitor should be not dropped by more than ± Δ/2
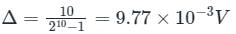
Δ/2 = 4.88 × 103 V
Maximum conversation time for the ADC is
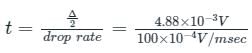
= 48.87 msec ≈ 49 msec

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
Question Description
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A signal channel signal acquisition system with 0-10 V range consist of a sample and hold circuit with worst case drop rate of 100 μV/ms and 10 bit ADC. The maximum conversion time for the ADC isa)49 msb)0.49 msc)4.9 msd)490 msCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.




















