Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A practical current source is usually represe...
Start Learning for Free
A practical current source is usually represented by
- a)A resistance in series with an ideal current source
- b)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current source
- c)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in ...
Introduction:
A practical current source is a device that provides a constant current regardless of the load connected to it. It is commonly used in electronic circuits to drive LEDs, transistors, and other devices that require a constant current for proper operation. In order to represent a practical current source, it is necessary to combine it with other circuit elements, such as resistors, to account for the characteristics and limitations of the source.
Explanation:
The correct representation of a practical current source is a resistance in parallel with an ideal current source. This means that the practical current source is connected in parallel with a resistor. Let's understand why this representation is appropriate:
1. Ideal current source:
An ideal current source is a theoretical concept that provides a constant current regardless of the load or external factors. It is represented by a short circuit symbol in circuit diagrams. However, in practical applications, it is not possible to achieve a perfect constant current source.
2. Resistance in parallel:
By connecting a resistance in parallel with the ideal current source, we can account for the limitations of the practical current source. The resistance represents the internal resistance of the source and the resistance of the load connected to it. When a load is connected to the current source, the voltage across the resistance causes a drop in the current. This drop can be modeled by the resistor in parallel.
3. Equivalent circuit:
The combination of the ideal current source and the resistance in parallel forms an equivalent circuit that accurately represents the behavior of the practical current source. This representation allows us to analyze the circuit and calculate the current flowing through the load based on the voltage across the resistance.
4. Alternative representations:
The other options mentioned in the question (resistance in series with an ideal current source, resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source, and none of the above) do not accurately represent the behavior of a practical current source. A resistance in series with an ideal current source would cause a drop in the current, which is not characteristic of a constant current source. A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source would result in a variable current depending on the load connected to the source. None of the above options accurately represent the behavior of a practical current source.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a practical current source is represented by a resistance in parallel with an ideal current source. This representation accurately models the behavior of the practical current source, taking into account the internal resistance and the load connected to it.
A practical current source is a device that provides a constant current regardless of the load connected to it. It is commonly used in electronic circuits to drive LEDs, transistors, and other devices that require a constant current for proper operation. In order to represent a practical current source, it is necessary to combine it with other circuit elements, such as resistors, to account for the characteristics and limitations of the source.
Explanation:
The correct representation of a practical current source is a resistance in parallel with an ideal current source. This means that the practical current source is connected in parallel with a resistor. Let's understand why this representation is appropriate:
1. Ideal current source:
An ideal current source is a theoretical concept that provides a constant current regardless of the load or external factors. It is represented by a short circuit symbol in circuit diagrams. However, in practical applications, it is not possible to achieve a perfect constant current source.
2. Resistance in parallel:
By connecting a resistance in parallel with the ideal current source, we can account for the limitations of the practical current source. The resistance represents the internal resistance of the source and the resistance of the load connected to it. When a load is connected to the current source, the voltage across the resistance causes a drop in the current. This drop can be modeled by the resistor in parallel.
3. Equivalent circuit:
The combination of the ideal current source and the resistance in parallel forms an equivalent circuit that accurately represents the behavior of the practical current source. This representation allows us to analyze the circuit and calculate the current flowing through the load based on the voltage across the resistance.
4. Alternative representations:
The other options mentioned in the question (resistance in series with an ideal current source, resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source, and none of the above) do not accurately represent the behavior of a practical current source. A resistance in series with an ideal current source would cause a drop in the current, which is not characteristic of a constant current source. A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage source would result in a variable current depending on the load connected to the source. None of the above options accurately represent the behavior of a practical current source.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a practical current source is represented by a resistance in parallel with an ideal current source. This representation accurately models the behavior of the practical current source, taking into account the internal resistance and the load connected to it.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in ...
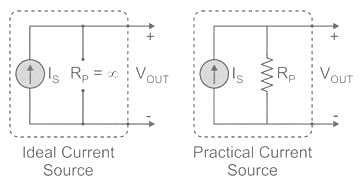
Ideal Current Source: An ideal voltage source has infinite resistance. Infinite resistance is equivalent to zero conductance. So, an ideal current source has zero conductance.
Practical Current Source: A practical current source is equivalent to an ideal current source in parallel with high resistance or low conductance.
Ideal and practical current sources are represented as shown in the below figure.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A practical current source is usually represented bya)A resistance in series with an ideal current sourceb)A resistance in parallel with an ideal current sourcec)A resistance in parallel with an ideal voltage sourced)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























