Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The theorem which states that in any linear, ...
Start Learning for Free
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called as
- a)Tellegen’s theorem
- b)Compensation theorem
- c)reciprocity theorem
- d)superposition theorem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, acti...
Tellegen theorem can be applied to any network- linear or non-linear, active or passive, time-variant, or time-invariant.
Tellegen Theorem: According to Tellegen’s theorem, the summation of instantaneous powers for the n number of branches in an electrical network is zero.
Let n number of branches in an electrical network have I1, I2, I3, …. In respective instantaneous currents through them.
These branches have instantaneous voltages across them are V1, V2, V3, …. Vn respectively.
Tellegen Theorem: According to Tellegen’s theorem, the summation of instantaneous powers for the n number of branches in an electrical network is zero.
Let n number of branches in an electrical network have I1, I2, I3, …. In respective instantaneous currents through them.
These branches have instantaneous voltages across them are V1, V2, V3, …. Vn respectively.
According to Tellegen’s theorem:
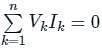
It is based on the conservation of energy and is applicable to both linear and non-linear circuits.
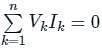
It is based on the conservation of energy and is applicable to both linear and non-linear circuits.
Important Points


Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, acti...
Explanation:
Tellegen's Theorem:
Tellegen's theorem states that in any linear or non-linear, passive or active, time-variant or time-invariant network, the algebraic sum of instantaneous powers at any instant in time is always zero.
Key Points:
- The theorem is named after Bernard Tellegen, a Dutch electrical engineer.
- It is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is used to analyze and understand the power flow in a network.
- The theorem is based on the conservation of energy principle, stating that the total power entering a network at any instant must be equal to the total power leaving the network.
- Tellegen's theorem can be applied to both AC and DC circuits, making it a versatile tool in circuit analysis.
- The theorem is essential for power system analysis, as it helps in determining power losses and optimizing the efficiency of electrical networks.
- Tellegen's theorem is used in various applications, including power distribution systems, signal processing, and electronic circuit design.
Conclusion:
Tellegen's theorem is a powerful tool in circuit analysis that helps in understanding and analyzing power flow in electrical networks. It is a fundamental principle that applies to a wide range of networks and is essential for engineers working in the field of electrical engineering.
Tellegen's Theorem:
Tellegen's theorem states that in any linear or non-linear, passive or active, time-variant or time-invariant network, the algebraic sum of instantaneous powers at any instant in time is always zero.
Key Points:
- The theorem is named after Bernard Tellegen, a Dutch electrical engineer.
- It is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is used to analyze and understand the power flow in a network.
- The theorem is based on the conservation of energy principle, stating that the total power entering a network at any instant must be equal to the total power leaving the network.
- Tellegen's theorem can be applied to both AC and DC circuits, making it a versatile tool in circuit analysis.
- The theorem is essential for power system analysis, as it helps in determining power losses and optimizing the efficiency of electrical networks.
- Tellegen's theorem is used in various applications, including power distribution systems, signal processing, and electronic circuit design.
Conclusion:
Tellegen's theorem is a powerful tool in circuit analysis that helps in understanding and analyzing power flow in electrical networks. It is a fundamental principle that applies to a wide range of networks and is essential for engineers working in the field of electrical engineering.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called asa)Tellegen’s theoremb)Compensation theoremc)reciprocity theoremd)superposition theoremCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























