Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > A system with a unity gain margin and zero ph...
Start Learning for Free
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____
- a)sluggish
- b)highly stable
- c)oscillatory
- d)relatively stable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)slug...
Unity Gain Margin (UGM) and Phase Margin (PM) are two important parameters used to analyze the stability of a control system.
Unity Gain Margin refers to the amount of gain that can be added to the system before it becomes unstable, while Phase Margin refers to the amount of phase lag that can be added to the system before it becomes unstable.
In this case, the system has a unity gain margin, which means that the system is on the verge of instability. This implies that any further increase in gain will cause the system to become unstable.
Zero Phase Margin means that the system has no phase lag before it becomes unstable. A zero phase margin indicates that the system is oscillatory in nature, meaning it will exhibit sustained oscillations or ringing behavior.
Hence, the correct answer is option C - oscillatory.
Here is a detailed explanation of each option:
a) Sluggish: Sluggishness refers to a slow response. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin do not imply sluggishness.
b) Highly stable: A highly stable system would have a large gain margin and a large phase margin. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin indicate that the system is on the verge of instability, so it is not highly stable.
c) Oscillatory: As mentioned earlier, a zero phase margin indicates that the system is oscillatory in nature. It will exhibit sustained oscillations or ringing behavior. Hence, this option is correct.
d) Relatively stable: Relatively stable refers to a system that is stable but with a small margin of stability. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin indicate that the system is on the verge of instability, so it is not relatively stable.
Unity Gain Margin refers to the amount of gain that can be added to the system before it becomes unstable, while Phase Margin refers to the amount of phase lag that can be added to the system before it becomes unstable.
In this case, the system has a unity gain margin, which means that the system is on the verge of instability. This implies that any further increase in gain will cause the system to become unstable.
Zero Phase Margin means that the system has no phase lag before it becomes unstable. A zero phase margin indicates that the system is oscillatory in nature, meaning it will exhibit sustained oscillations or ringing behavior.
Hence, the correct answer is option C - oscillatory.
Here is a detailed explanation of each option:
a) Sluggish: Sluggishness refers to a slow response. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin do not imply sluggishness.
b) Highly stable: A highly stable system would have a large gain margin and a large phase margin. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin indicate that the system is on the verge of instability, so it is not highly stable.
c) Oscillatory: As mentioned earlier, a zero phase margin indicates that the system is oscillatory in nature. It will exhibit sustained oscillations or ringing behavior. Hence, this option is correct.
d) Relatively stable: Relatively stable refers to a system that is stable but with a small margin of stability. A unity gain margin and zero phase margin indicate that the system is on the verge of instability, so it is not relatively stable.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)slug...
- Gain margin (GM): The gain margin of the system defines by how much the system gain can be increased so that the system moves on the edge of stability.
- It is determined from the gain at the phase cross-over frequency.
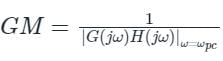
- Phase crossover frequency (ωpc): It is the frequency at which the phase angle of G(s) H(s) is -180°.

- Phase margin (PM): The phase margin of the system defines by how much the phase of the system can increase to make the system unstable.
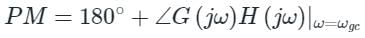
- It is determined from the phase at the gain cross over frequency.
- Gain crossover frequency (ωgc): It is the frequency at which the magnitude of G(s) H(s) is unity.
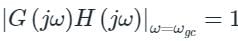
- So it is important to note that these margins of stability are valid for open-loop stable systems only.
- A large gain margin or a large phase margin indicates a very stable feedback system but usually a very sluggish response.
- Hence a Gain margin close to unity (or 0 in dB) or a phase margin close to zero corresponds to a highly oscillatory system.
Hence option (3) is the correct answer.
Gain margin and phase margin are frequently used for frequency response specifications by designers. Usually a Gain margin of about 6 dB or a Phase margin of 30 - 35° results in a reasonably good degree of relative stability.
Important Points
Gain margin and phase margin are frequently used for frequency response specifications by designers. Usually a Gain margin of about 6 dB or a Phase margin of 30 - 35° results in a reasonably good degree of relative stability.
Important Points
- If both GM and PM are positive, the system is stable (ωgc < ωpc)
- If both GM and PM are negative, the system is unstable (ωgc > ωpc)
- If both GM and PM are zero, the system is just stable (ωgc = ωpc)

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Question Description
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A system with a unity gain margin and zero phase margin is _____a)sluggishb)highly stablec)oscillatoryd)relatively stableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























