Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Directions: A horizontal gas engine running ...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.
What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)
Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of ...
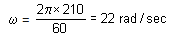
For slider-crank mechanism,
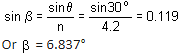
Force on the piston due to gas pressure,
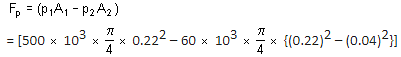
= 19007 – 2206 = 16,801 N
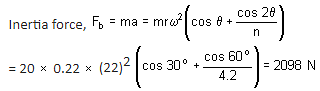
Piston effort, F = Fp – Fb
= 16801 – 2098 = 14,703 N
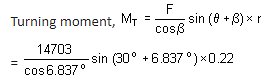
= 1953 N–m
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of ...
Given:
- Engine speed (N) = 210 rpm
- Bore (D) = 220 mm
- Stroke (L) = 440 mm
- Connecting rod length (R) = 924 mm
- Reciprocating parts weight (W) = 20 kg
- Gas pressure on the cover side (Pc) = 500 kN/m2
- Gas pressure on the crank side (Pcr) = 60 kN/m2
- Piston rod diameter (d) = 40 mm
To Find:
Turning moment on the crankshaft (M)
Assumptions:
- The engine is running at a steady state.
- The gas pressure is constant throughout the crank rotation.
- Frictional losses are neglected.
Solution:
1. Calculate the piston area (A) using the bore diameter:
- A = π/4 * D^2
2. Calculate the piston rod area (Ar) using the rod diameter:
- Ar = π/4 * d^2
3. Calculate the crank radius (r) using the stroke and connecting rod length:
- r = L + (R/2)
4. Calculate the force on the piston (Fp) due to gas pressure on the cover side:
- Fp = Pc * A
5. Calculate the force on the crank (Fc) due to gas pressure on the crank side:
- Fc = Pcr * Ar
6. Calculate the angle turned by the crank (θ) from the inner dead center:
- θ = (30/360) * 2π
7. Calculate the horizontal component of the force on the crank (Fcx):
- Fcx = Fc * cos(θ)
8. Calculate the vertical component of the force on the crank (Fcy):
- Fcy = Fc * sin(θ)
9. Calculate the moment arm (Marm) due to the horizontal force on the crank:
- Marm = r * sin(θ)
10. Calculate the moment arm (Marp) due to the vertical force on the crank:
- Marp = R * sin(θ)
11. Calculate the moment due to the horizontal force on the crank (Mx):
- Mx = Fcx * Marm
12. Calculate the moment due to the vertical force on the crank (My):
- My = Fcy * Marp
13. Calculate the total moment on the crankshaft (M):
- M = Mx + My
Substituting the Given Values:
- N = 210 rpm
- D = 220 mm
- L = 440 mm
- R = 924 mm
- W = 20 kg
- Pc = 500 kN/m2
- Pcr = 60 kN/m2
- d = 40 mm
Calculations:
1. A = π/4 * (0.22)^2 = 0.0385 m2
2. Ar = π/4 * (0.04)^2 = 0.0013 m2
3. r = 0.44 + (0.924/2) = 0.932 m
4. Fp = 500 * 10
- Engine speed (N) = 210 rpm
- Bore (D) = 220 mm
- Stroke (L) = 440 mm
- Connecting rod length (R) = 924 mm
- Reciprocating parts weight (W) = 20 kg
- Gas pressure on the cover side (Pc) = 500 kN/m2
- Gas pressure on the crank side (Pcr) = 60 kN/m2
- Piston rod diameter (d) = 40 mm
To Find:
Turning moment on the crankshaft (M)
Assumptions:
- The engine is running at a steady state.
- The gas pressure is constant throughout the crank rotation.
- Frictional losses are neglected.
Solution:
1. Calculate the piston area (A) using the bore diameter:
- A = π/4 * D^2
2. Calculate the piston rod area (Ar) using the rod diameter:
- Ar = π/4 * d^2
3. Calculate the crank radius (r) using the stroke and connecting rod length:
- r = L + (R/2)
4. Calculate the force on the piston (Fp) due to gas pressure on the cover side:
- Fp = Pc * A
5. Calculate the force on the crank (Fc) due to gas pressure on the crank side:
- Fc = Pcr * Ar
6. Calculate the angle turned by the crank (θ) from the inner dead center:
- θ = (30/360) * 2π
7. Calculate the horizontal component of the force on the crank (Fcx):
- Fcx = Fc * cos(θ)
8. Calculate the vertical component of the force on the crank (Fcy):
- Fcy = Fc * sin(θ)
9. Calculate the moment arm (Marm) due to the horizontal force on the crank:
- Marm = r * sin(θ)
10. Calculate the moment arm (Marp) due to the vertical force on the crank:
- Marp = R * sin(θ)
11. Calculate the moment due to the horizontal force on the crank (Mx):
- Mx = Fcx * Marm
12. Calculate the moment due to the vertical force on the crank (My):
- My = Fcy * Marp
13. Calculate the total moment on the crankshaft (M):
- M = Mx + My
Substituting the Given Values:
- N = 210 rpm
- D = 220 mm
- L = 440 mm
- R = 924 mm
- W = 20 kg
- Pc = 500 kN/m2
- Pcr = 60 kN/m2
- d = 40 mm
Calculations:
1. A = π/4 * (0.22)^2 = 0.0385 m2
2. Ar = π/4 * (0.04)^2 = 0.0013 m2
3. r = 0.44 + (0.924/2) = 0.932 m
4. Fp = 500 * 10
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions: A horizontal gas engine running at 210 rpm has a bore of 220 mm and a stroke of 440 mm. The connecting rod is 924 mm long and the reciprocating parts weigh 20 kg. When the crank has turned through an angle of 30° from the inner dead centre, the gas pressure on the cover and the crank sides are 500 kN/m2 and 60 kN/m2, respectively. The diameter of the piston rod is 40 mm.What will be the turning moment (in N-m) on the crank shaft? (to the nearest integer)Correct answer is '1953'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























