Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its...
Start Learning for Free
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correct
- a)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMC
- b)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMC
- c)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteria
- d)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteria
Correct answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the...
Compaction of Soil and its Application
Overview:
Soil compaction is the process of applying mechanical energy to soil in order to remove air voids and increase its density. It is an important process in construction, as compacted soil provides better load-bearing capacity and stability. The compaction of soil is influenced by several factors such as moisture content, compaction effort, soil type, and compaction criteria. In certain applications, such as the construction of earth dams, different compaction criteria are used.
Compaction of Earth Core:
- The core of the earth, which is the central part of an earth dam, is compacted on the wet side of the optimum moisture content (OMC).
- The OMC is the moisture content at which the soil achieves maximum compaction and minimum voids. Compacting the earth core on the wet side of the OMC ensures better compaction and reduced permeability.
- The presence of moisture helps in the rearrangement of soil particles, resulting in better compaction and higher density.
Compaction of Homogeneous Dams:
- Homogeneous dams are compacted on the dry side of the OMC.
- The OMC for homogeneous dams is lower than that of the earth core. Compacting the soil on the dry side of the OMC helps to achieve a higher density and lower permeability.
- Dry compaction of homogeneous dams ensures that the moisture content is reduced to a level where the soil particles can be closely packed, resulting in improved strength and reduced seepage.
Governing Criteria:
- The compaction of the earth core is primarily governed by strength criteria.
- Strength criteria refer to the ability of the compacted soil to withstand external loads and maintain its stability.
- A higher density achieved through compaction helps in improving the strength of the core material, making it suitable for load-bearing purposes.
- The compaction of homogeneous dams is primarily governed by permeability criteria.
- Permeability criteria refer to the ability of the compacted soil to resist the flow of water through it.
- Compacting the soil on the dry side of the OMC helps to reduce the permeability of the soil, ensuring that there is minimal seepage through the dam.
Conclusion:
In summary, the compaction of the earth core is done on the wet side of the OMC, and it is governed by strength criteria. On the other hand, homogeneous dams are compacted on the dry side of the OMC, and their compaction is governed by permeability criteria. These different approaches to compaction ensure that the soil achieves the desired properties for its specific application, whether it is load-bearing or seepage control.
Overview:
Soil compaction is the process of applying mechanical energy to soil in order to remove air voids and increase its density. It is an important process in construction, as compacted soil provides better load-bearing capacity and stability. The compaction of soil is influenced by several factors such as moisture content, compaction effort, soil type, and compaction criteria. In certain applications, such as the construction of earth dams, different compaction criteria are used.
Compaction of Earth Core:
- The core of the earth, which is the central part of an earth dam, is compacted on the wet side of the optimum moisture content (OMC).
- The OMC is the moisture content at which the soil achieves maximum compaction and minimum voids. Compacting the earth core on the wet side of the OMC ensures better compaction and reduced permeability.
- The presence of moisture helps in the rearrangement of soil particles, resulting in better compaction and higher density.
Compaction of Homogeneous Dams:
- Homogeneous dams are compacted on the dry side of the OMC.
- The OMC for homogeneous dams is lower than that of the earth core. Compacting the soil on the dry side of the OMC helps to achieve a higher density and lower permeability.
- Dry compaction of homogeneous dams ensures that the moisture content is reduced to a level where the soil particles can be closely packed, resulting in improved strength and reduced seepage.
Governing Criteria:
- The compaction of the earth core is primarily governed by strength criteria.
- Strength criteria refer to the ability of the compacted soil to withstand external loads and maintain its stability.
- A higher density achieved through compaction helps in improving the strength of the core material, making it suitable for load-bearing purposes.
- The compaction of homogeneous dams is primarily governed by permeability criteria.
- Permeability criteria refer to the ability of the compacted soil to resist the flow of water through it.
- Compacting the soil on the dry side of the OMC helps to reduce the permeability of the soil, ensuring that there is minimal seepage through the dam.
Conclusion:
In summary, the compaction of the earth core is done on the wet side of the OMC, and it is governed by strength criteria. On the other hand, homogeneous dams are compacted on the dry side of the OMC, and their compaction is governed by permeability criteria. These different approaches to compaction ensure that the soil achieves the desired properties for its specific application, whether it is load-bearing or seepage control.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the...
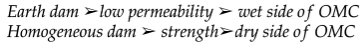

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Question Description
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Pertaining to the compaction of soil and its application which of the following is/are correcta)core of earth is compacted on wet side of OMCb)homogeneous dams are compacted on dry side of OMCc)compaction core of earth is governed by strength criteriad)homogeneous dams compaction is governed by permeability criteriaCorrect answer is option 'A, B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















