Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines ...
Start Learning for Free
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)
Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypoch...
Explanation:
1. Introduction
Chlorine gas (Cl2) is commonly used for disinfection due to its strong oxidizing properties. When chlorine gas is added to water, it reacts with water molecules to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). The equilibrium between HOCl and hypochlorite ion (OCl-) is governed by the pH of the solution.
2. Equilibrium Reaction
The equilibrium reaction between HOCl and OCl- can be represented as follows:
HOCl ⇔ H+ + OCl-
3. Equilibrium Constant (k)
The equilibrium constant (k) for the above reaction is given as 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C. The value of k indicates the extent to which the reaction proceeds in the forward or backward direction. A smaller value of k suggests that the reaction favors the backward direction.
4. Relationship with pH
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. It is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) present in the solution. In the case of the equilibrium reaction between HOCl and OCl-, the concentration of H+ ions affects the equilibrium position.
5. Fraction of HOCl
The fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual can be calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
pH = pKa + log([OCl-]/[HOCl])
where pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) for the reaction.
6. Calculation
In this case, the pKa value can be calculated using the equation:
pKa = -log(k) = -log(2.7 × 10-8) ≈ 7.57
Substituting the pKa value into the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, we get:
6.6 = 7.57 + log([OCl-]/[HOCl])
Simplifying the equation, we can solve for the ratio of [OCl-]/[HOCl]:
log([OCl-]/[HOCl]) = 6.6 - 7.57 = -0.97
[OCl-]/[HOCl] = 10^(-0.97) ≈ 0.120
The fraction of HOCl is given by:
Fraction of HOCl = [HOCl]/([HOCl] + [OCl-]) ≈ [HOCl]/(0.120[HOCl]) = 1/0.120 ≈ 0.90
Therefore, the 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of 6.6.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual can be determined using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. At a pH value of 6.6, approximately 90% of the free chlorine residual exists as HOCl, making it a more effective disinfectant.
1. Introduction
Chlorine gas (Cl2) is commonly used for disinfection due to its strong oxidizing properties. When chlorine gas is added to water, it reacts with water molecules to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). The equilibrium between HOCl and hypochlorite ion (OCl-) is governed by the pH of the solution.
2. Equilibrium Reaction
The equilibrium reaction between HOCl and OCl- can be represented as follows:
HOCl ⇔ H+ + OCl-
3. Equilibrium Constant (k)
The equilibrium constant (k) for the above reaction is given as 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C. The value of k indicates the extent to which the reaction proceeds in the forward or backward direction. A smaller value of k suggests that the reaction favors the backward direction.
4. Relationship with pH
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. It is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) present in the solution. In the case of the equilibrium reaction between HOCl and OCl-, the concentration of H+ ions affects the equilibrium position.
5. Fraction of HOCl
The fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual can be calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
pH = pKa + log([OCl-]/[HOCl])
where pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) for the reaction.
6. Calculation
In this case, the pKa value can be calculated using the equation:
pKa = -log(k) = -log(2.7 × 10-8) ≈ 7.57
Substituting the pKa value into the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, we get:
6.6 = 7.57 + log([OCl-]/[HOCl])
Simplifying the equation, we can solve for the ratio of [OCl-]/[HOCl]:
log([OCl-]/[HOCl]) = 6.6 - 7.57 = -0.97
[OCl-]/[HOCl] = 10^(-0.97) ≈ 0.120
The fraction of HOCl is given by:
Fraction of HOCl = [HOCl]/([HOCl] + [OCl-]) ≈ [HOCl]/(0.120[HOCl]) = 1/0.120 ≈ 0.90
Therefore, the 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of 6.6.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual can be determined using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. At a pH value of 6.6, approximately 90% of the free chlorine residual exists as HOCl, making it a more effective disinfectant.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypoch...
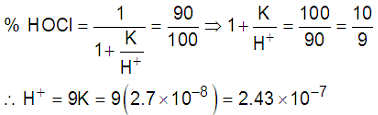
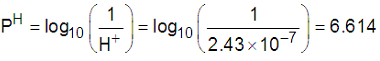
= 6.6

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Chlorine gas used for disinfection combines with water to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl). HOCl ionises to form hypochlorite (OCl-) in a reversible reaction: HOCI ⇔ H+ + OCl- (k= 2.7 × 10-8 at 20 °C), the equilibrium of which is governed by pH. The sum of HOCI and OCl- is known as free chlorine residual and HOCI is more effective disinfectant. The 90% fraction of HOCl in the free chlorine residual is available at a pH value of (Answer up to one decimal place)Correct answer is '6.6'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























