Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > The electrical system shown in figure, conv...
Start Learning for Free
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .
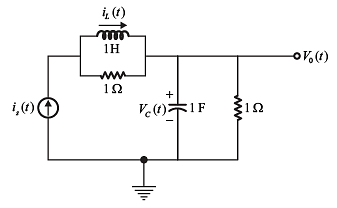
Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system is
- a)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.
- b)Completely state controllable but not observable.
- c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.
- d)Neither state controllable nor observable.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current...
Given circuit is shown below,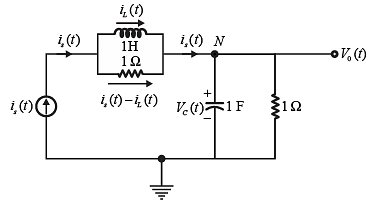

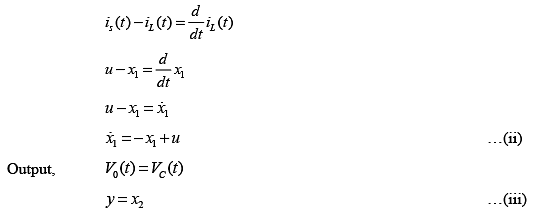
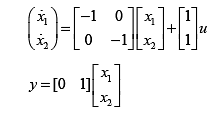
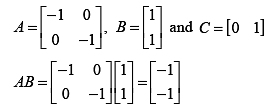
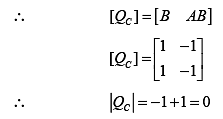
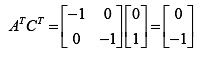
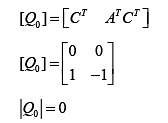
View all questions of this test

Assume, iL(t) = x1 → First state variable
VC (t) = x2 → Second state variable
is (t) = u → Input of system
and V0 (t) = y → Output of system
Apply KCL at node N,

KVL in the loop between inductor and resistor,
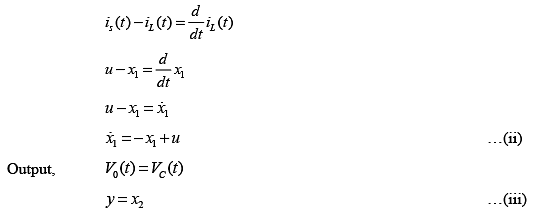
From equation (i), (ii) and (iii), state variable modal can be written as,
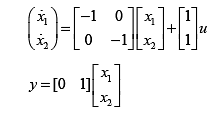
Thus matrices A, B, and C are,
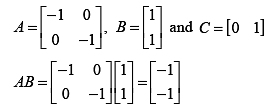
Condition of controllability,
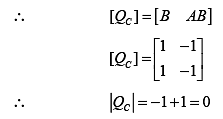
Thus, system is uncontrollable.
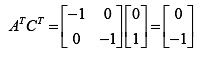
Condition of observability,
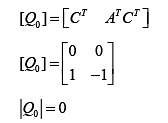
Thus, system is un-observable.
So, the system is neither controllable nor observable.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Most Upvoted Answer
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current...
Given circuit is shown below,

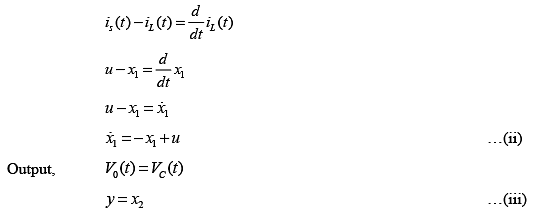
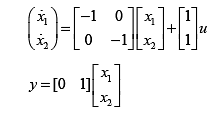
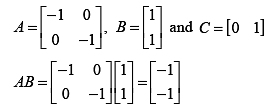
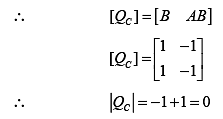
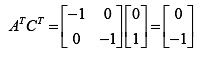
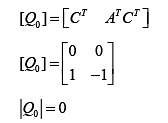

Assume, iL(t) = x1 → First state variable
VC (t) = x2 → Second state variable
is (t) = u → Input of system
and V0 (t) = y → Output of system
Apply KCL at node N,

KVL in the loop between inductor and resistor,
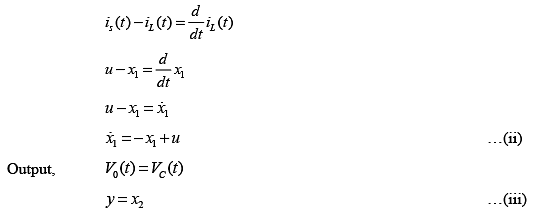
From equation (i), (ii) and (iii), state variable modal can be written as,
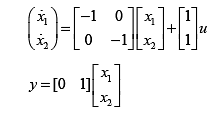
Thus matrices A, B, and C are,
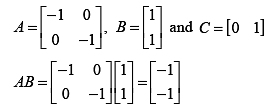
Condition of controllability,
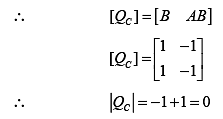
Thus, system is uncontrollable.
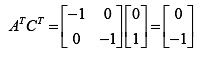
Condition of observability,
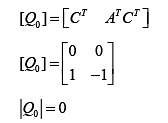
Thus, system is un-observable.
So, the system is neither controllable nor observable.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The electrical system shown in figure, converts input source current is(t) to output voltageV0(t) .Current iL(t) in the inductor and voltage VC (t) across the capacitor are taken as the state variables, both assumed to be initially equal to zero i.e. iL (0) = 0 and VC (0) = 0 . The system isa)Completely state controllable as well as completely observable.b)Completely state controllable but not observable.c)Completely state observable but not state controllable.d)Neither state controllable nor observable.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























