Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission...
Start Learning for Free
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)
Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line induc...
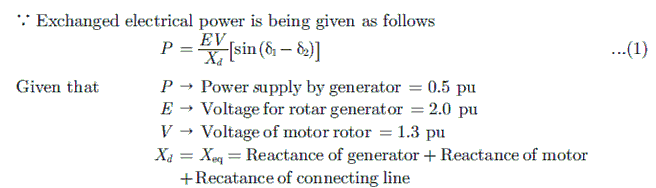
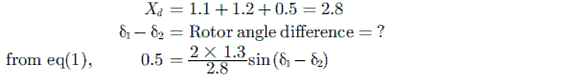
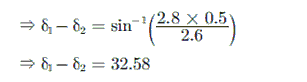
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line induc...
Introduction:
In an HVDC transmission system, the rotor angle difference refers to the phase difference between the AC and DC voltages. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and efficient operation of the system. The rotor angle difference is influenced by various factors, including the auxiliary components used in the HVDC system.
Auxiliary Components:
The two auxiliary components that significantly impact the rotor angle difference in an HVDC transmission system are the DC line inductor and the reactive power sources. Let's understand the role of each component in detail:
1. DC Line Inductor:
- The DC line inductor is connected in series with the DC transmission line.
- It is used to limit the rate of change of current during transient conditions, such as faults or switching events.
- The inductor helps to dampen the oscillations and stabilize the system.
- It reduces the impact of sudden changes in DC current on the AC system and helps maintain a stable rotor angle difference.
2. Reactive Power Sources:
- Reactive power sources, such as static compensators or synchronous condensers, are used to regulate the voltage and reactive power flow in the system.
- They provide reactive power support and help maintain the desired voltage levels.
- By controlling the reactive power flow, these sources can influence the rotor angle difference.
- Increasing or decreasing the reactive power support can change the rotor angle difference and affect the system's stability.
Calculation of Rotor Angle Difference:
The given answer states that the rotor angle difference is 32.58 degrees. However, the calculation method or specific system parameters are not provided. Therefore, it is difficult to explain the answer in detail without further information.
To calculate the rotor angle difference accurately, various system parameters such as the DC line inductance, AC system parameters, and reactive power support need to be considered. The specific system configuration and control strategy will determine the exact impact of these auxiliary components on the rotor angle difference.
In conclusion, the rotor angle difference in an HVDC transmission system is influenced by auxiliary components such as the DC line inductor and reactive power sources. These components play a vital role in maintaining system stability and voltage control. The given answer of 32.58 degrees represents the calculated rotor angle difference, but without additional information, it is challenging to explain the answer in detail.
In an HVDC transmission system, the rotor angle difference refers to the phase difference between the AC and DC voltages. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and efficient operation of the system. The rotor angle difference is influenced by various factors, including the auxiliary components used in the HVDC system.
Auxiliary Components:
The two auxiliary components that significantly impact the rotor angle difference in an HVDC transmission system are the DC line inductor and the reactive power sources. Let's understand the role of each component in detail:
1. DC Line Inductor:
- The DC line inductor is connected in series with the DC transmission line.
- It is used to limit the rate of change of current during transient conditions, such as faults or switching events.
- The inductor helps to dampen the oscillations and stabilize the system.
- It reduces the impact of sudden changes in DC current on the AC system and helps maintain a stable rotor angle difference.
2. Reactive Power Sources:
- Reactive power sources, such as static compensators or synchronous condensers, are used to regulate the voltage and reactive power flow in the system.
- They provide reactive power support and help maintain the desired voltage levels.
- By controlling the reactive power flow, these sources can influence the rotor angle difference.
- Increasing or decreasing the reactive power support can change the rotor angle difference and affect the system's stability.
Calculation of Rotor Angle Difference:
The given answer states that the rotor angle difference is 32.58 degrees. However, the calculation method or specific system parameters are not provided. Therefore, it is difficult to explain the answer in detail without further information.
To calculate the rotor angle difference accurately, various system parameters such as the DC line inductance, AC system parameters, and reactive power support need to be considered. The specific system configuration and control strategy will determine the exact impact of these auxiliary components on the rotor angle difference.
In conclusion, the rotor angle difference in an HVDC transmission system is influenced by auxiliary components such as the DC line inductor and reactive power sources. These components play a vital role in maintaining system stability and voltage control. The given answer of 32.58 degrees represents the calculated rotor angle difference, but without additional information, it is challenging to explain the answer in detail.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer?.
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Auxiliary components in an HVDC transmission system are DC line inductor and reactive power sources. Find the rotor angle difference (in degrees). (Answer up to two decimal places)Correct answer is '32.58'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























