Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000...
Start Learning for Free
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?
- a)1.5
- b)1.6
Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a p...
Calculation of Received Power
Given parameters:
Distance between spacecrafts = 3000 km
Diameter of parabolic reflector antenna = 0.85 m
Frequency of operation = 2 GHz
Aperture efficiency = 64%
Receiver requirement for 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio = 1 pW
The received power at spacecraft A can be calculated using the Friis transmission equation:
Pr = Pt * Gt * Gr * ((λ / 4πd)^2) * Ae
Where,
Pr = Received power
Pt = Transmitted power
Gt = Gain of transmitting antenna
Gr = Gain of receiving antenna
λ = Wavelength of signal
d = Distance between transmitting and receiving antennas
Ae = Effective aperture of receiving antenna
Wavelength can be calculated using the formula:
λ = c / f
Where,
c = Speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s)
f = Frequency of operation
Substituting the given values:
λ = 3 x 10^8 / 2 x 10^9 = 0.15 m
Effective aperture can be calculated using the formula:
Ae = (π * D^2 * η) / 4
Where,
D = Diameter of antenna
η = Aperture efficiency
Substituting the given values:
Ae = (π * 0.85^2 * 0.64) / 4 = 0.362 m^2
The gain of an antenna is given by:
G = (4π * Ae) / λ^2
Substituting the given values for spacecraft A:
Ae = 0.362 m^2
λ = 0.15 m
G = (4π * 0.362) / (0.15)^2 = 106.38
The received power can now be calculated using the Friis transmission equation:
Pr = Pt * Gt * Gr * ((λ / 4πd)^2) * Ae
Assuming the gain of the antennas on both spacecrafts to be the same, i.e., Gr = Gt = 106.38, and substituting the given values:
Pr = Pt * 106.38^2 * ((0.15 / 4π * 3000000)^2) * 0.362
Pr = 3.7 x 10^-22 * Pt
Calculation of Required Transmitted Power
The required transmitted power on spacecraft B can be calculated using the following formula:
Pt = (Pr * SNR) / k
Where,
SNR = Signal-to-noise ratio
k = Boltzmann's constant (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K)
Substituting the given values:
SNR = 10^(20/10) = 100
k = 1.38 x 10^-23
Pt = (3.7 x 10^-22 * Pt * 100) / (1.38 x 10^-23)
Solving for Pt:
Pt = 1.5 W (approximately)
Therefore, the required transmitted power on spacecraft B to achieve a signal-to-noise ratio of 20 dB at spacecraft A is approximately 1.5 W.
Given parameters:
Distance between spacecrafts = 3000 km
Diameter of parabolic reflector antenna = 0.85 m
Frequency of operation = 2 GHz
Aperture efficiency = 64%
Receiver requirement for 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio = 1 pW
The received power at spacecraft A can be calculated using the Friis transmission equation:
Pr = Pt * Gt * Gr * ((λ / 4πd)^2) * Ae
Where,
Pr = Received power
Pt = Transmitted power
Gt = Gain of transmitting antenna
Gr = Gain of receiving antenna
λ = Wavelength of signal
d = Distance between transmitting and receiving antennas
Ae = Effective aperture of receiving antenna
Wavelength can be calculated using the formula:
λ = c / f
Where,
c = Speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s)
f = Frequency of operation
Substituting the given values:
λ = 3 x 10^8 / 2 x 10^9 = 0.15 m
Effective aperture can be calculated using the formula:
Ae = (π * D^2 * η) / 4
Where,
D = Diameter of antenna
η = Aperture efficiency
Substituting the given values:
Ae = (π * 0.85^2 * 0.64) / 4 = 0.362 m^2
The gain of an antenna is given by:
G = (4π * Ae) / λ^2
Substituting the given values for spacecraft A:
Ae = 0.362 m^2
λ = 0.15 m
G = (4π * 0.362) / (0.15)^2 = 106.38
The received power can now be calculated using the Friis transmission equation:
Pr = Pt * Gt * Gr * ((λ / 4πd)^2) * Ae
Assuming the gain of the antennas on both spacecrafts to be the same, i.e., Gr = Gt = 106.38, and substituting the given values:
Pr = Pt * 106.38^2 * ((0.15 / 4π * 3000000)^2) * 0.362
Pr = 3.7 x 10^-22 * Pt
Calculation of Required Transmitted Power
The required transmitted power on spacecraft B can be calculated using the following formula:
Pt = (Pr * SNR) / k
Where,
SNR = Signal-to-noise ratio
k = Boltzmann's constant (1.38 x 10^-23 J/K)
Substituting the given values:
SNR = 10^(20/10) = 100
k = 1.38 x 10^-23
Pt = (3.7 x 10^-22 * Pt * 100) / (1.38 x 10^-23)
Solving for Pt:
Pt = 1.5 W (approximately)
Therefore, the required transmitted power on spacecraft B to achieve a signal-to-noise ratio of 20 dB at spacecraft A is approximately 1.5 W.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a p...
R = 3000km = 3 × 106m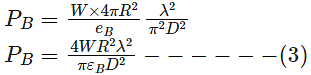
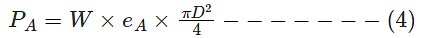
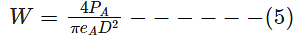
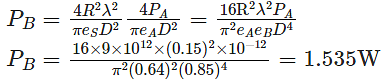
Diameter of antenna,
D = 0.85m λ = c/f = (3 × 1013)/(2 × 109) = 0.15m
Power required far receiving antenna
A, PA = 1pW = 10−12W
For SNR = 20dB = 100
Gain of the antenna B,GB = 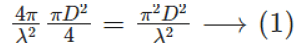
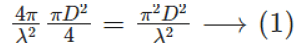
Power density from B,W = 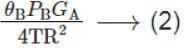
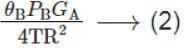
Where, PB is the power transmitted by B¯.
Aperture efficiency, eA = eB =64%
Operating frequency, f = 2GHz From (1) and (2)
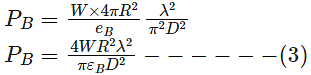
Power received at the transmitting antenna,
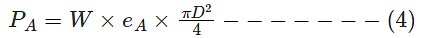
From eq (4)
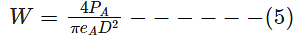
From E.q. (3) and E.q.(5)
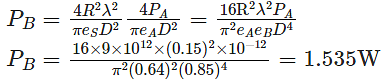
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer?.
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The distance between two spacecrafts is 3000 km. Both of them has a paraboidal reflector antenna of 0.85m diameter which operates at a frequency of 2 GHz, with an aperture efficiency of 64 %. If the spacecraft A’s receiver requires 1 pW for a 20 dB signal-to-noise ratio then what transmitted power (in Watts)is required on the spacecraft B to achieve this signal-to-noise ratio ?a)1.5b)1.6Correct answer is between '1.5,1.6'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























