Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid leve...
Start Learning for Free
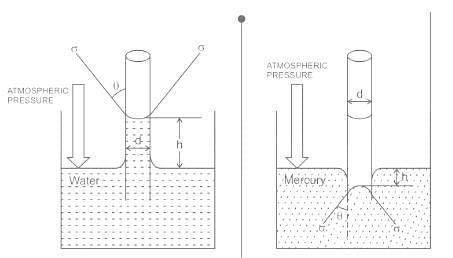
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?
- a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.
- b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.
- c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.
- d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube i...
Cohesion vs Adhesion in Non-wetting Liquids like Mercury
Understanding the relationship between cohesion and adhesion in non-wetting liquids like mercury is crucial in explaining the capillarity phenomenon.
Cohesion in Mercury
- Cohesion refers to the attraction between molecules of the same substance. In the case of mercury, cohesion is strong due to the presence of metallic bonds between mercury atoms.
- Mercury molecules exhibit a high degree of cohesion, which causes them to stick together and form a compact liquid body.
Adhesion between Mercury and Capillary Tube
- Adhesion, on the other hand, is the attraction between molecules of different substances. In the case of mercury and a capillary tube, adhesion plays a significant role.
- The adhesion between mercury and the capillary tube surface is relatively weaker compared to the cohesion within the mercury itself.
- As a result, the cohesive forces within the mercury dominate over the adhesive forces between mercury and the tube.
Relation between Cohesion and Adhesion
- In the context of non-wetting liquids like mercury, the cohesion within the liquid is greater than the adhesion between the liquid and the solid surface of the capillary tube.
- This imbalance in forces leads to the rise of mercury in the capillary tube, as the cohesive forces pull the liquid up against the weaker adhesive forces.
- Therefore, in the case of mercury, cohesion is greater than adhesion, which results in the unique capillarity behavior observed in non-wetting liquids.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube i...
- In case of mercury used in capillary tube cohesive force is predominates, so it does not wet the glass.
- Cohesive forces are force of attraction between molecules of same type.
- Adhesive forces are force of attraction between molecules of different type.
- In case of water adhesive force is stronger than cohesive force that's why it wet the glass.
- In case of mercury, due to higher angle of contact between glass & mercury ie θ > 90°, the meniscus formed is convex. Thus, cohesive force between mercury molecules is stronger, and mercury column will tend to shrink rather than rising upwards

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The phenomenon of rise or fall of liquid level in a capillarity tube is called as capillarity. In non-wetting liquids (e.g. mercury), what is the relation between cohesion of mercury and adhesion between mercury and capillary tube?a)Cohesion is lesser than adhesion.b)Cohesion is equal to adhesion.c)No relation between cohesion and adhesion.d)Cohesion is greater than adhesion.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























