SAT Exam > SAT Questions > Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in t...
Start Learning for Free
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.
The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.
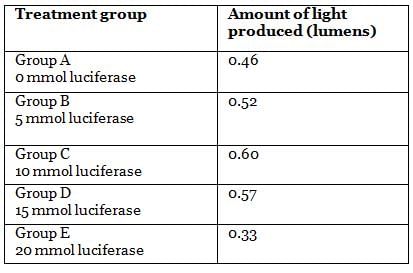
To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.
The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.
To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.

Q. The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.
- a)hopeful and motivated
- b)disappointed and critical
- c)enthusiastic and surprised
- d)informed and precise
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae incl...
indication that the author has any positive or negative emotions toward these figures. As the reader, it might be natural to feel hopeful or motivated to improve the efficiency of our everyday lights to match that of the fireflies, but be careful not to extrapolate unless told to do so.

|
Explore Courses for SAT exam
|

|
Similar SAT Doubts
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SAT 2025 is part of SAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SAT exam syllabus. Information about Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SAT 2025 is part of SAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SAT exam syllabus. Information about Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Individuals of the roughly 2,000 species in the family Lampyridae include those insects capable of producing bioluminescent light through a specific metabolic process. Though commonly referred to as fireflies or lightning bugs, these idiosyncratic creatures are more accurately categorized as winged beetles. Like their amphibian predators, most fireflies are crepuscular and are thus largely reliant on their bioluminescence to attract mates, find food, and warn predators of their potential poisonousness. Fireflies are known not to be desirable prey animals for most predators due to the presence of potentially harmful substances in their blood and bitter taste. During their larval stage, bioluminescence serves as the primary defense mechanism to fend off those predators. The diet of most fireflies includes a mixture of nectar, pollen, fireflies, and other insects. It has been shown that different species of fireflies exhibit unique bioluminescence patterns when attracting mates. For example, males of the species P. pyralis (the state insect of Tennessee) use flashing patterns during courtship to attract potential mates. If a female elects to mate with the male, she will respond by reciprocating with a flash of her own. However, the males must beware, as females of other species such as P. pensylvanica can mimic these patterns to deceive, attract, and eat the males.The biochemical reaction by which fireflies produce light occurs inside a specialized organ in their lower abdomen. This light-emitting organ utilizes the molecule luciferin, which is responsible for the production of visible light. In the presence of oxygen, magnesium ions, and the energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the enzyme luciferase converts luciferin into oxyluciferin, which emits light due to being in an electronically excited state. Upon emitting light, oxyluciferin is recycled and reconverted to luciferin so the process may continue. As with any biochemical process, the rate and capacity for bioluminescence in fireflies is dictated by the concentration of inputs as well as the rate at which byproducts are recycled. Scientists still do not fully understand how fireflies are able to produce bioluminescence with upwards of 80-90% energy efficiency. In comparison, the average incandescent light bulbs and LED lights emit only about 10% and 20% of their total electrical energy input as light, respectively. Since the first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of the universe is constant and energy can neither be created nor destroyed, heat is the major byproduct in the reactions mentioned above.To further study the interaction of firefly luciferase with its substrate, a student designs an experiment testing the rate at which the molecules involved are recycled. The student gathers 100 fireflies and separates them randomly into five equal experimental groups. Group A is not given any treatment and each subsequent group of fireflies is administered increasing concentrations of luciferin. Each group of fireflies is then released into separate pitch-black rooms that mimic the fireflies’ natural habitat. These rooms also contain light meters that measure the intensity of light emitted by the group of 20 fireflies as a whole. The results of this experiment are shown in Table 1.Q.The author’s tone in the underlined portion of the passage is best described as __________.a)hopeful and motivatedb)disappointed and criticalc)enthusiastic and surprisedd)informed and preciseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for SAT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























