BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Questions > Liver damage is caused due to the overdose o...
Start Learning for Free
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?
- a)Vitamin B5
- b)Vitamin B12
- c)Vitamin B3
- d)Vitamin D
- e)None of the above/More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin...
Liver damage can be caused by various factors, including excessive alcohol consumption, drug abuse, and certain medical conditions. However, in the context of this question, liver damage is specifically associated with an overdose of Vitamin B3, also known as niacin.
Niacin is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It is involved in numerous physiological processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and hormone synthesis. Niacin is also important for maintaining healthy skin, nervous system, and digestive system.
However, taking excessive amounts of niacin supplements can have detrimental effects on the liver. This is primarily due to the fact that niacin is metabolized in the liver and excreted through bile. When an excessive amount of niacin is consumed, it can overwhelm the liver's metabolic capacity, leading to liver damage.
The mechanism by which niacin overdose causes liver damage is not completely understood. It is believed that the accumulation of niacin and its metabolites in the liver can disrupt cellular processes and cause oxidative stress, leading to inflammation and damage to liver cells.
Symptoms of liver damage caused by niacin overdose may include abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, fatigue, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, it can progress to liver failure.
To prevent liver damage, it is important to consume niacin within the recommended daily intake levels. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for niacin varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. For adults, the RDA ranges from 14-16 mg for women and 16-18 mg for men.
It is worth noting that niacin obtained from natural food sources is generally safe and does not pose a risk of liver damage. Foods rich in niacin include meat, fish, poultry, legumes, whole grains, and nuts. However, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any dietary supplements, including niacin, to ensure proper dosage and avoid potential complications.
Niacin is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It is involved in numerous physiological processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and hormone synthesis. Niacin is also important for maintaining healthy skin, nervous system, and digestive system.
However, taking excessive amounts of niacin supplements can have detrimental effects on the liver. This is primarily due to the fact that niacin is metabolized in the liver and excreted through bile. When an excessive amount of niacin is consumed, it can overwhelm the liver's metabolic capacity, leading to liver damage.
The mechanism by which niacin overdose causes liver damage is not completely understood. It is believed that the accumulation of niacin and its metabolites in the liver can disrupt cellular processes and cause oxidative stress, leading to inflammation and damage to liver cells.
Symptoms of liver damage caused by niacin overdose may include abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, fatigue, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, it can progress to liver failure.
To prevent liver damage, it is important to consume niacin within the recommended daily intake levels. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for niacin varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. For adults, the RDA ranges from 14-16 mg for women and 16-18 mg for men.
It is worth noting that niacin obtained from natural food sources is generally safe and does not pose a risk of liver damage. Foods rich in niacin include meat, fish, poultry, legumes, whole grains, and nuts. However, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any dietary supplements, including niacin, to ensure proper dosage and avoid potential complications.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin...
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose Vitamin B3.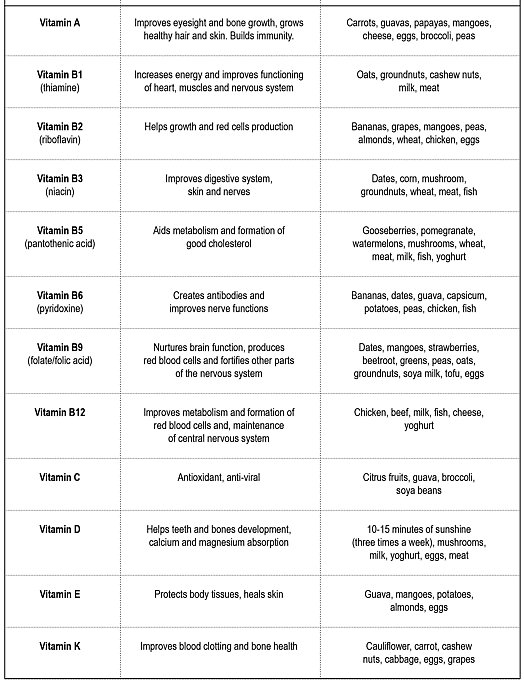
Related points
- A vitamin is an organic molecule that is an essential micronutrient which an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism.
- Based on the solubility, Vitamins have been classified into two different groups:
- Fat-soluble vitamin
- Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the fat cells and as the name suggests, these vitamins require fat in order to be absorbed. Vitamin A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble vitamins.
- Water-soluble vitamin
- Water-soluble vitamins are not stored in our body as their excess gets excreted through the urine. Therefore, these vitamins need to be replenished constantly. Vitamin B and C are water-soluble vitamins.
Other points

Attention BPSC (Bihar) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed BPSC (Bihar) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in BPSC (Bihar).

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
Similar BPSC (Bihar) Doubts
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for BPSC (Bihar).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?a)Vitamin B5b)Vitamin B12c)Vitamin B3d)Vitamin De)None of the above/More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice BPSC (Bihar) tests.

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Test: Human Environment Interactions the Tropical and The Subtropical Region
Test | 15 questions
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























