CDS Exam > CDS Questions > Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrop...
Start Learning for Free
Food chain is:
- a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.
- b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.
- c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.
- d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange ...
Food Chain is the transfer of food energy from producers like plants through a series of organisms, where each stage is accompanied by one eating the other.
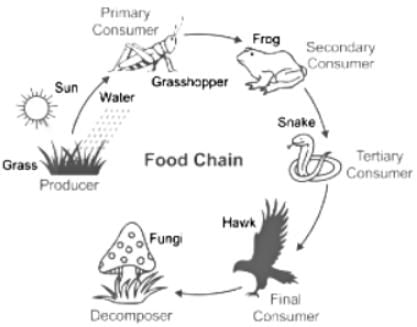

- Every step is called the 'trophic level'.
- There are two types of food chains - Detritus food chain, and the Grazing food chain.
- About 90% of energy is lost after each trophic level.
- Thus, only 10% of the energy is transferred.

Most Upvoted Answer
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange ...
The correct answer is option 'C': the food chain refers to the passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another. Let's explore this answer in detail:
Definition of a Food Chain:
A food chain is a sequence of organisms that are interconnected by their feeding habits. It represents the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another within an ecosystem.
Explanation of the Answer:
The answer 'C) Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another' is correct because a food chain describes the transfer of food energy from one organism to another. It shows how energy moves through different trophic levels (feeding levels) in an ecosystem.
Components of a Food Chain:
A food chain typically consists of three main components:
1. Producers: The first level of a food chain includes autotrophic organisms, such as plants or algae, which produce their own food through photosynthesis. They convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (a form of energy-rich organic compound).
2. Consumers: The second level consists of heterotrophic organisms that consume the producers or other consumers for energy. Consumers can be classified into different categories based on their feeding habits:
a. Primary consumers (herbivores): These organisms feed directly on plants or algae.
b. Secondary consumers (carnivores): They prey on primary consumers.
c. Tertiary consumers (top carnivores): They feed on secondary consumers.
d. Omnivores: These organisms consume both plants and animals.
3. Decomposers: The final level includes decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi. They break down the dead organic matter and return nutrients back to the soil, completing the cycle.
Flow of Energy:
The food chain illustrates the transfer of energy from one organism to another. The energy initially captured by the producers through photosynthesis is passed on to the primary consumers when they consume the producers. Likewise, the energy is transferred to the higher-level consumers as they feed on the lower-level consumers.
Significance of Food Chains:
Food chains are vital for the stability and functioning of ecosystems. They help in understanding the interdependence of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. Disruptions or imbalances in food chains can have significant impacts on the population dynamics of organisms and the overall health of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the food chain represents the passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another. It is an essential concept in ecology that helps us comprehend the interconnections and energy flow within ecosystems.
Definition of a Food Chain:
A food chain is a sequence of organisms that are interconnected by their feeding habits. It represents the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another within an ecosystem.
Explanation of the Answer:
The answer 'C) Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another' is correct because a food chain describes the transfer of food energy from one organism to another. It shows how energy moves through different trophic levels (feeding levels) in an ecosystem.
Components of a Food Chain:
A food chain typically consists of three main components:
1. Producers: The first level of a food chain includes autotrophic organisms, such as plants or algae, which produce their own food through photosynthesis. They convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (a form of energy-rich organic compound).
2. Consumers: The second level consists of heterotrophic organisms that consume the producers or other consumers for energy. Consumers can be classified into different categories based on their feeding habits:
a. Primary consumers (herbivores): These organisms feed directly on plants or algae.
b. Secondary consumers (carnivores): They prey on primary consumers.
c. Tertiary consumers (top carnivores): They feed on secondary consumers.
d. Omnivores: These organisms consume both plants and animals.
3. Decomposers: The final level includes decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi. They break down the dead organic matter and return nutrients back to the soil, completing the cycle.
Flow of Energy:
The food chain illustrates the transfer of energy from one organism to another. The energy initially captured by the producers through photosynthesis is passed on to the primary consumers when they consume the producers. Likewise, the energy is transferred to the higher-level consumers as they feed on the lower-level consumers.
Significance of Food Chains:
Food chains are vital for the stability and functioning of ecosystems. They help in understanding the interdependence of organisms and the flow of energy within an ecosystem. Disruptions or imbalances in food chains can have significant impacts on the population dynamics of organisms and the overall health of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the food chain represents the passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another. It is an essential concept in ecology that helps us comprehend the interconnections and energy flow within ecosystems.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange ...
Food Chain is the transfer of food energy from producers like plants through a series of organisms, where each stage is accompanied by one eating the other.


- Every step is called the 'trophic level'.
- There are two types of food chains - Detritus food chain, and the Grazing food chain.
- About 90% of energy is lost after each trophic level.
- Thus, only 10% of the energy is transferred.


|
Explore Courses for CDS exam
|

|
Question Description
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for CDS 2025 is part of CDS preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CDS exam syllabus. Information about Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CDS 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for CDS 2025 is part of CDS preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CDS exam syllabus. Information about Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CDS 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for CDS.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CDS Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Food chain is:a)Relationship between autotrophic organisms.b)Exchange of genetic material between two organisms.c)Passage of food (and thus energy) from one organism to another.d)Modern enterpreneur establishment providing food outlets.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice CDS tests.

|
Explore Courses for CDS exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.




























