ACT Exam > ACT Questions > Directions:Read the passages and choose the b...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.
Passage
Radon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.
Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.
The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.
Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.
Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).
A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.
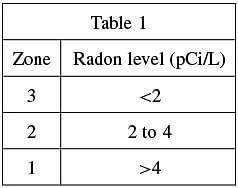
Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.
Passage
Radon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.
Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.
The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.
Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.
Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).
A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.
Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.

Q. According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?
- a)5.2 pCi/L
- b)4.0 pCi/L
- c)3.0 pCi/L
- d)1.9 pCi/L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each questi...
The best answer is A. Radon potential is defined as “an estimate of the radon level of a structure.” According to the passage, Zone 1 includes areas with a high radon potential. Table 1 indicates that the pCi/L levels in Zone 1 are greater than 4. Therefore, a radon level of 5.2 pCi/L would be considered the most harmful.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Similar ACT Doubts
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for ACT 2025 is part of ACT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. Information about Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for ACT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions:Read the passages and choose the best answer to each question.PassageRadon is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment as a result of the decay of uranium. If inhaled into the lungs at high concentrations and over a long period of time, radon gas can increase the chance that an individual will develop lung cancer.Outdoors, radon levels are rarely high enough to pose a health threat to individuals. Indoors, however, radon is a concern because it can seep into the foundation of a home through the ground and accumulate in areas with little ventilation, where levels can then become threatening. Radon gas can seep from the ground through many different pathways, such as cracks in the basement floor, through drains and sump pumps, or through loose-fitting pipes.The only way to detect radon levels is through testing, using a specialized sensing device. Radon is colorless and odorless, and the levels are constantly changing from one area to the next and from one day to the next. In addition, radon exposure produces no short-term health symptoms.Therefore, radon levels should be monitored on a regular basis.Radon potential is an estimate of the radon level of a structure measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).A picocurie is one-trillionth of a Curie (a measurement unit of radioactivity). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) assigns each county in the United States to a zone, based on its radon potential. Radon potential is not used to determine which houses should be tested in an area.Instead, levels are used to determine if radon-resistant features should be installed in new structures being built in an area. Table 1 shows the radon levels in pCi/L for each of 3 zones, with areas in Zone 1 indicating a high radon potential, areas in Zone 2 indicating a moderate radon potential, and areas in Zone 3 indicating a low radon potential.Q.According to the passage, which of the following radon levels would be considered most harmful?a)5.2 pCi/Lb)4.0 pCi/Lc)3.0 pCi/Ld)1.9 pCi/LCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice ACT tests.

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























