BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Questions > Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields...
Start Learning for Free
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?
- a)Iron
- b)Potassium
- c)Nitrogen
- d)Phosphorus
- e)None of the above / More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all n...
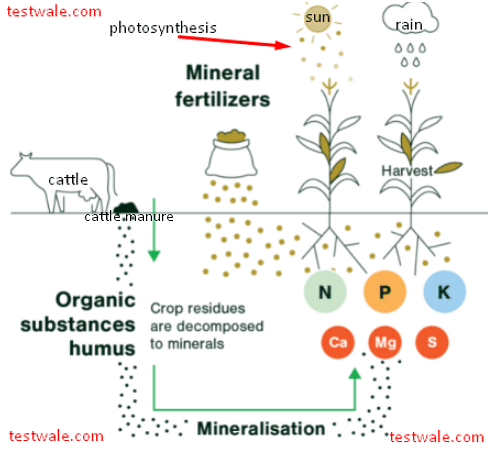
Plants need nutrients to grow which they absorb from the soil via the plant’s root system.
- Fertilizers provide the major nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and important secondary elements) that plants need.
Nitrogen fertilizers
- Nitrate-based fertilizers are the most commonly used straight fertilizers include ammonium sulphate and ammonium sulphate nitrate, calcium nitrate, sodium nitrate, Chilean nitrate and anhydrous ammonia.
- The main products are nitrate-based fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate (AN) and calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN), which are well suited to soils and climatic conditions, and urea ammonium nitrate (UAN) aqueous solution.
- Nitrogen is the main constituent of chlorophyll that maintains a balance in the process of photosynthesis
Phosphorus fertilizers
- The most common phosphate fertilizers are single superphosphate (SSP), triple superphosphate (TSP), monoammonium phosphate (MAP), di-ammonium phosphate (DSP) and ammonium polyphosphate liquid.
Potassium fertilizers
- Potassium is also available in a range of fertilizers which contain potassium only or two or more nutrients and include Potassium chloride (KCl), Potassium sulphate (K2SO4) or sulphate of potash (SOP), Potassium nitrate (KNO3), known as KN.
Why iron nutrient is usually not available in fertilizers
- In soil, Iron, it is often ineffective, especially in pH above 7.0, because iron quickly transforms to Fe3+ and precipitates as one of the iron oxides.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all n...
Answer:
Introduction:
Fertilizers are substances that are added to the soil or plants to provide essential nutrients for their growth and development. They are commonly used in agriculture to improve soil fertility and obtain higher yields of crops. However, not all nutrients necessary for plant growth are available in fertilizers.
Explanation:
Among the given options, iron (Fe) is the nutrient that is usually not available in fertilizers.
Iron (Fe):
Iron is an essential micronutrient required by plants for various physiological processes, including chlorophyll synthesis, respiration, and enzyme activation. It plays a crucial role in the transfer of energy and the metabolism of nitrogen. However, iron is often present in the soil in an insoluble form, making it less available for plant uptake.
Why is iron usually not available in fertilizers?
1. Insufficient concentration: Iron is required by plants in small amounts, and its concentration in fertilizers is usually insufficient to meet the plant's requirements.
2. Complexation: Iron can form complexes with other compounds in the soil, making it less available for plant uptake.
3. Low solubility: Iron compounds have low solubility in water, which restricts their availability to plants.
How to address iron deficiency in plants?
To address iron deficiency in plants, various strategies can be employed:
1. Iron chelates: Iron chelates, such as iron ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), are commonly used to supply available iron to plants. These chelates enhance the solubility and availability of iron in the soil.
2. Foliar application: Iron can be supplied to plants through foliar application. Iron-containing compounds are sprayed on the foliage, allowing direct absorption by the leaves.
3. Soil amendments: Adding organic matter or substances such as sulfur or organic acids to the soil can help improve iron availability by reducing its insoluble forms.
4. Soil pH adjustment: Iron availability is influenced by soil pH. Acidic soils (pH below 7) favor iron solubility and uptake by plants. Adjusting soil pH can improve iron availability.
Conclusion:
While fertilizers are valuable for providing essential nutrients to plants, they may not contain all the necessary nutrients. Iron, an essential micronutrient, is usually not available in fertilizers due to its low concentration, complexation, and low solubility in water. Iron deficiency in plants can be addressed through the use of iron chelates, foliar application, soil amendments, and soil pH adjustment.
Attention BPSC (Bihar) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed BPSC (Bihar) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in BPSC (Bihar).

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
Similar BPSC (Bihar) Doubts
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for BPSC (Bihar).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Fertilizers are used to obtain higher yields of crops. However, all nutrients are usually not available in fertilizers. Which one of the following nutrients is usually not available in fertilizers?a)Ironb)Potassiumc)Nitrogend)Phosphoruse)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice BPSC (Bihar) tests.

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Test: Human Environment Interactions the Tropical and The Subtropical Region
Test | 15 questions
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























