Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > The output impedance of a BJT under common-co...
Start Learning for Free
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration is
- a)low
- b)high
- c)medium
- d)very high
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa...
- Common collector configuration, also known as emitter follower provides high input impedance and low output impedance. So they are used for the purpose of impedance matching.
- In common collector configuration, the collector terminal is common to both input and output terminals.
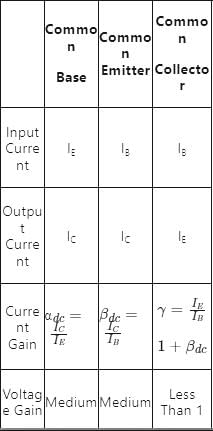
Important Differences between different transistor configuration is as shown:

Most Upvoted Answer
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa...
Output Impedance of a BJT under Common-Collector Configuration
The output impedance of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) in common-collector (CC) configuration is low. This means that the output impedance value is relatively small compared to other configurations.
Explanation:
In a common-collector configuration, the emitter terminal is common to both the input and output. The input is applied to the base terminal, and the output is taken from the collector terminal.
Characteristics of Common-Collector Configuration:
1. Voltage Gain: The common-collector configuration offers a voltage gain less than unity (less than 1). This configuration is also known as an emitter follower. The output voltage follows the input voltage, but with a slight voltage drop. This voltage gain is less than 1 due to the voltage division between the emitter resistor and the load resistor.
2. Current Gain: The common-collector configuration provides a current gain greater than unity (greater than 1). The base current and collector current are approximately equal, which results in a current gain greater than 1.
3. Input Impedance: The input impedance of the common-collector configuration is relatively high. This is because the base terminal is driven by a low-impedance source, and the emitter terminal is common to the input. The input impedance is primarily determined by the base-emitter junction.
4. Output Impedance: The output impedance of the common-collector configuration is low. This means that the output impedance value is relatively small compared to other configurations. The low output impedance is due to the emitter terminal being common to both the input and output. The output impedance is primarily determined by the collector-emitter junction.
5. Voltage Phase Relationship: The output voltage in the common-collector configuration is in-phase with the input voltage. This means that there is no phase inversion between the input and output signals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration is low. This is due to the emitter terminal being common to both the input and output, resulting in a relatively small output impedance value compared to other configurations.
The output impedance of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) in common-collector (CC) configuration is low. This means that the output impedance value is relatively small compared to other configurations.
Explanation:
In a common-collector configuration, the emitter terminal is common to both the input and output. The input is applied to the base terminal, and the output is taken from the collector terminal.
Characteristics of Common-Collector Configuration:
1. Voltage Gain: The common-collector configuration offers a voltage gain less than unity (less than 1). This configuration is also known as an emitter follower. The output voltage follows the input voltage, but with a slight voltage drop. This voltage gain is less than 1 due to the voltage division between the emitter resistor and the load resistor.
2. Current Gain: The common-collector configuration provides a current gain greater than unity (greater than 1). The base current and collector current are approximately equal, which results in a current gain greater than 1.
3. Input Impedance: The input impedance of the common-collector configuration is relatively high. This is because the base terminal is driven by a low-impedance source, and the emitter terminal is common to the input. The input impedance is primarily determined by the base-emitter junction.
4. Output Impedance: The output impedance of the common-collector configuration is low. This means that the output impedance value is relatively small compared to other configurations. The low output impedance is due to the emitter terminal being common to both the input and output. The output impedance is primarily determined by the collector-emitter junction.
5. Voltage Phase Relationship: The output voltage in the common-collector configuration is in-phase with the input voltage. This means that there is no phase inversion between the input and output signals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration is low. This is due to the emitter terminal being common to both the input and output, resulting in a relatively small output impedance value compared to other configurations.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The output impedance of a BJT under common-collector configuration isa)lowb)highc)mediumd)very highCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























