UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > The electric field intensity of a plane wave ...
Start Learning for Free
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by: 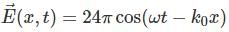 V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of 120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?
V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of 120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?
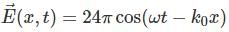 V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of 120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?
V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of 120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?- a)0.07 W
- b)0.03 W
- c)0.05 W
- d)0.04 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space ...
Concept:
The time-averaged pointing vector generally for Electric and magnetic fields in x and y direction is given by:
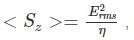 where Erms is the root mean square electric field amplitude. In free space with E(t) varying sinusoidally at some frequency with peak amplitude E0, its rms voltage is given by
where Erms is the root mean square electric field amplitude. In free space with E(t) varying sinusoidally at some frequency with peak amplitude E0, its rms voltage is given by 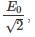 with the average Poynting vector then given by:
with the average Poynting vector then given by: 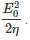
where η being the wave impedance.
Explanation:
We are given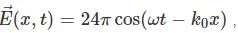
with the time averaged pointing vector is given by: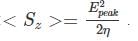
The wave impedance is given to be 120π
E0 is the peak electric field.
First, we should calculate the average pointing vector the electric field given.
Hence the average pointing vector is given by:
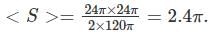
Now average power is given by:
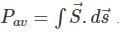 where ds is the unit area vector.
where ds is the unit area vector.
The plane which is given to us is x+y =1.
The unit normal to this plane is given by:
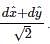
The average power is thus given by:
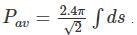 The integral over the elementary area is total area.
The integral over the elementary area is total area.
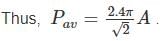
A is the total area which is given by;
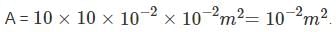
Thus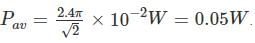
The time-averaged pointing vector generally for Electric and magnetic fields in x and y direction is given by:
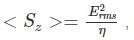 where Erms is the root mean square electric field amplitude. In free space with E(t) varying sinusoidally at some frequency with peak amplitude E0, its rms voltage is given by
where Erms is the root mean square electric field amplitude. In free space with E(t) varying sinusoidally at some frequency with peak amplitude E0, its rms voltage is given by 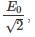 with the average Poynting vector then given by:
with the average Poynting vector then given by: 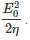
where η being the wave impedance.
Explanation:
We are given
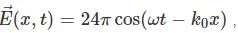
with the time averaged pointing vector is given by:
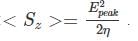
The wave impedance is given to be 120π
E0 is the peak electric field.
First, we should calculate the average pointing vector the electric field given.
Hence the average pointing vector is given by:
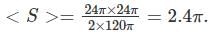
Now average power is given by:
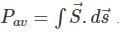 where ds is the unit area vector.
where ds is the unit area vector.The plane which is given to us is x+y =1.
The unit normal to this plane is given by:
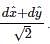
The average power is thus given by:
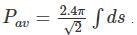 The integral over the elementary area is total area.
The integral over the elementary area is total area.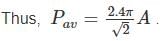
A is the total area which is given by;
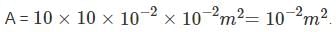
Thus
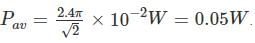

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Similar UGC NET Doubts
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The electric field intensity of a plane wave travelling in free space is given by:V/m. In this field consider a square area of 10 cm X 10 cm on a plane x+y =1 with wave impedance of120π120π. The total time averaged power (in W) passing through the square area is?a)0.07 Wb)0.03 Wc)0.05 Wd)0.04 WCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























