Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrea...
Start Learning for Free
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.
Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
Which of the following is correct?
Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
Which of the following is correct?
- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)A is false but R is true
- c)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
- d)A is true but R is false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in d...
The soil structure changes from flocculated to dispersed as the moisture content reached the optimum moisture content. In this case, due to the change in structure, the permeability decreases, and the dry density increases.
Flocculated structure:
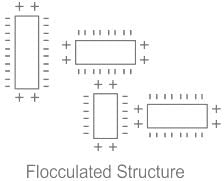
Flocculated structure:

- The interaction of soil particles is face-to-face.
- The attractive force generated.
Dispersed structure:
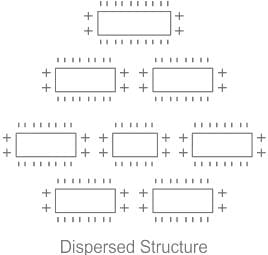

- The interaction of soil particles is face-to-face.
- The repulsive force generated.
- Seepage is less as compared to the flocculated structure.
Hence both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Most Upvoted Answer
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in d...
Permeability and Dry Density of Compacted Soil
Permeability is a measure of the ability of a soil to transmit water or other fluids through it. It is an important property in geotechnical engineering as it affects the flow of water through soil, which in turn influences the stability and behavior of structures built on or in the soil. The permeability of a soil is influenced by various factors, including the dry density of the compacted soil.
A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.
When a soil is compacted, its dry density increases due to the reduction in void spaces between the soil particles. As the dry density increases, the soil particles come closer together, resulting in a decrease in the size of the voids or pores within the soil. This reduction in pore size has a direct impact on the permeability of the soil.
R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
The behavior of soil particles in water surroundings is influenced by various forces, including electrostatic and van der Waals forces. These forces can cause soil particles to be mutually attracted or repulsed, depending on the nature of the particles and the presence of other ions or molecules in the water.
Explanation:
A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.
The decrease in permeability with an increase in dry density can be explained by the reduction in pore size and the increased interlocking of soil particles. As the void spaces between the particles decrease, the flow paths for water also become more restricted, leading to a decrease in permeability. The compacted soil has a higher resistance to the flow of water due to the reduced pore size, resulting in a lower permeability.
R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
The behavior of soil particles in water is influenced by various forces. When soil particles are in water surroundings, they can experience attractive or repulsive forces. These forces can be due to the presence of charged particles or ions in the water. Attraction or repulsion between soil particles can affect the arrangement and packing of particles, which in turn can influence the pore size and permeability of the soil.
Conclusion:
Both Assertion A and Reason R are true. The decrease in permeability with an increase in dry density of a compacted soil is due to the reduction in pore size and increased interlocking of soil particles. The behavior of soil particles in water surroundings can be influenced by attractive or repulsive forces, which can affect the arrangement and packing of particles and consequently impact the permeability of the soil.
Permeability is a measure of the ability of a soil to transmit water or other fluids through it. It is an important property in geotechnical engineering as it affects the flow of water through soil, which in turn influences the stability and behavior of structures built on or in the soil. The permeability of a soil is influenced by various factors, including the dry density of the compacted soil.
A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.
When a soil is compacted, its dry density increases due to the reduction in void spaces between the soil particles. As the dry density increases, the soil particles come closer together, resulting in a decrease in the size of the voids or pores within the soil. This reduction in pore size has a direct impact on the permeability of the soil.
R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
The behavior of soil particles in water surroundings is influenced by various forces, including electrostatic and van der Waals forces. These forces can cause soil particles to be mutually attracted or repulsed, depending on the nature of the particles and the presence of other ions or molecules in the water.
Explanation:
A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.
The decrease in permeability with an increase in dry density can be explained by the reduction in pore size and the increased interlocking of soil particles. As the void spaces between the particles decrease, the flow paths for water also become more restricted, leading to a decrease in permeability. The compacted soil has a higher resistance to the flow of water due to the reduced pore size, resulting in a lower permeability.
R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.
The behavior of soil particles in water is influenced by various forces. When soil particles are in water surroundings, they can experience attractive or repulsive forces. These forces can be due to the presence of charged particles or ions in the water. Attraction or repulsion between soil particles can affect the arrangement and packing of particles, which in turn can influence the pore size and permeability of the soil.
Conclusion:
Both Assertion A and Reason R are true. The decrease in permeability with an increase in dry density of a compacted soil is due to the reduction in pore size and increased interlocking of soil particles. The behavior of soil particles in water surroundings can be influenced by attractive or repulsive forces, which can affect the arrangement and packing of particles and consequently impact the permeability of the soil.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Assertion A: Permeability continues to decrease with the increase in dry density of a compacted soil.Reason R: Soil particles in water surroundings may be mutually attracted or repulsed.Which of the following is correct?a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)A is false but R is truec)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of Ad)A is true but R is falseCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























