UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > The structure obtained when all the tetrahedr...
Start Learning for Free
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the type
- a)NaCl
- b)CsCl
- c)CaF2
- d)ZnS
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in ...
- In a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure, the atoms are located at each corner and in the center of each face of the cube. A close packing arrangement of atoms typically found in metal crystals, an fcc unit cell has 8 atoms at the corners and 6 atoms at the face centers, for a total equivalent of 4 whole atoms per unit cell.
- Now, in the arrangement of this lattice, there are voids or holes between the atoms where other, smaller atoms can fit. There are two main types of holes in a close-packed structure -- octahedral holes and tetrahedral holes.
- In the fcc lattice, the number of tetrahedral holes is twice the number of atoms. That is, for each atom in the lattice, there are 2 tetrahedral holes. This means in an fcc structure with N atoms, there are 2N tetrahedral holes.
- Considering the structure of CaF2:
- The Ca2+ ions form a face-centered cubic lattice. This means there are N Ca2+ ions.
- The F- ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in this lattice. Because there are 2N tetrahedral holes for N Ca2+ ions, this produces 2N F- ions.
- Thus, the calcium ions (Ca2+) make up an fcc lattice, and the fluoride ions (F-) fit into all of the tetrahedral holes, giving a 1:2 ratio of Ca2+:F-, which matches the formula for calcium fluoride, CaF2.
- Each calcium ion in the crystal structure is coordinated by 8 fluorides forming a cube, and each fluoride ion is coordinated tetrahedrally by 4 calcium ions. This results in a highly ordered, three-dimensional arrangement of particles that makes up the crystalline structure of CaF2
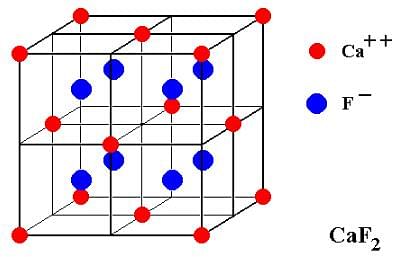
So, the structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the type is CaF2.
Most Upvoted Answer
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in ...
Answer:
When all the tetrahedral holes in a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure are occupied, the resulting structure is of the type CaF2. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
FCC Structure:
The face-centered cubic (fcc) structure is one of the most common crystal structures in solid materials. In an fcc structure, the atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with additional atoms located at the centers of each face. This results in a close-packed arrangement of atoms, with each atom surrounded by 12 nearest neighbors.
Tetrahedral Holes:
In an fcc structure, there are two types of voids or holes between the atoms. These are known as tetrahedral holes and octahedral holes. The tetrahedral holes are located at the centers of the tetrahedrons formed by the four nearest neighbor atoms. Each tetrahedral hole is surrounded by four nearest neighbor atoms.
Occupation of Tetrahedral Holes:
When all the tetrahedral holes in an fcc structure are occupied, the resulting structure becomes the type CaF2. In this structure, the cations occupy the lattice points of the fcc structure, while the anions occupy the tetrahedral holes.
CaF2 Structure:
The CaF2 structure is a common crystal structure observed in ionic compounds. In this structure, the cations (Ca2+) occupy the fcc lattice points, and the anions (F-) occupy all the tetrahedral holes. Each Ca2+ ion is surrounded by 8 F- ions, and each F- ion is surrounded by 4 Ca2+ ions.
Explanation:
When all the tetrahedral holes in an fcc structure are occupied, the resulting structure is similar to the CaF2 structure. This is because the occupation of tetrahedral holes by anions in an fcc structure is a characteristic feature of the CaF2 structure. Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'C' (CaF2).
To summarize, when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in an fcc structure, the resulting structure is of the type CaF2, with cations occupying the fcc lattice points and anions occupying the tetrahedral holes.
When all the tetrahedral holes in a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure are occupied, the resulting structure is of the type CaF2. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
FCC Structure:
The face-centered cubic (fcc) structure is one of the most common crystal structures in solid materials. In an fcc structure, the atoms are arranged in a cubic lattice with additional atoms located at the centers of each face. This results in a close-packed arrangement of atoms, with each atom surrounded by 12 nearest neighbors.
Tetrahedral Holes:
In an fcc structure, there are two types of voids or holes between the atoms. These are known as tetrahedral holes and octahedral holes. The tetrahedral holes are located at the centers of the tetrahedrons formed by the four nearest neighbor atoms. Each tetrahedral hole is surrounded by four nearest neighbor atoms.
Occupation of Tetrahedral Holes:
When all the tetrahedral holes in an fcc structure are occupied, the resulting structure becomes the type CaF2. In this structure, the cations occupy the lattice points of the fcc structure, while the anions occupy the tetrahedral holes.
CaF2 Structure:
The CaF2 structure is a common crystal structure observed in ionic compounds. In this structure, the cations (Ca2+) occupy the fcc lattice points, and the anions (F-) occupy all the tetrahedral holes. Each Ca2+ ion is surrounded by 8 F- ions, and each F- ion is surrounded by 4 Ca2+ ions.
Explanation:
When all the tetrahedral holes in an fcc structure are occupied, the resulting structure is similar to the CaF2 structure. This is because the occupation of tetrahedral holes by anions in an fcc structure is a characteristic feature of the CaF2 structure. Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option 'C' (CaF2).
To summarize, when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in an fcc structure, the resulting structure is of the type CaF2, with cations occupying the fcc lattice points and anions occupying the tetrahedral holes.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The structure obtained when all the tetrahedral holes are occupied in a fcc structure is of the typea)NaClb)CsClc)CaF2d)ZnSCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























