Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A capacitor used for power factor correction ...
Start Learning for Free
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:
- a)the line current and increases power factor
- b)both line current and power factor
- c)line current
- d)power factor
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit d...
Power factor improvement using the static capacitor:
Consider an inductive load taking a lagging current 'I' at a power factor cos ϕ1.
In order to improve the power factor of this circuit, the remedy is to connect such equipment in parallel with the load which takes a leading reactive component and partly cancels the lagging reactive component of the load.
The below figure shows a capacitor connected across the load.
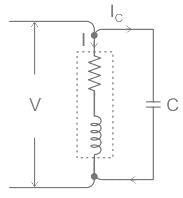
The capacitor takes a current Ic which leads the supply voltage V by 90°. The current Ic partly cancels the lagging reactive component of the load current as shown in the phasor diagram.
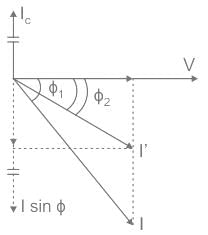

The capacitor takes a current Ic which leads the supply voltage V by 90°. The current Ic partly cancels the lagging reactive component of the load current as shown in the phasor diagram.

The resultant circuit current becomes I′ and its angle is ϕ2.
It is clear that ϕ2 is less than ϕ1 so the new p.f. cos ϕ2 is more than the previous p.f. cos ϕ1.
The resultant circuit current I′ is less than I.
It is clear that ϕ2 is less than ϕ1 so the new p.f. cos ϕ2 is more than the previous p.f. cos ϕ1.
The resultant circuit current I′ is less than I.
Most Upvoted Answer
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit d...
Understanding Power Factor Correction
Power factor correction is an essential technique used in electrical systems to enhance efficiency. In a single-phase circuit, capacitors are commonly employed for this purpose.
Function of Capacitors in Power Factor Correction
- Capacitors provide reactive power, which can counteract the inductive effects in a circuit.
- The presence of inductive loads (like motors) causes the current to lag behind the voltage, resulting in a low power factor.
Effects of Adding a Capacitor
1. Decrease in Line Current:
- Adding a capacitor reduces the total reactive power demand of the circuit.
- As reactive power is diminished, the overall current drawn from the supply reduces since the line current is proportional to the total apparent power (S = V * I).
2. Increase in Power Factor:
- The power factor (PF) is defined as the ratio of real power (P) to apparent power (S).
- By improving the balance between real and reactive power through the addition of capacitors, the power factor increases.
- A higher power factor indicates more efficient utilization of electrical power.
Conclusion
In summary, the use of a capacitor for power factor correction in a single-phase circuit effectively decreases the line current while simultaneously increasing the power factor. Hence, the correct answer is option 'A'. This enhancement leads to improved energy efficiency and reduced electricity costs in power distribution systems.
Power factor correction is an essential technique used in electrical systems to enhance efficiency. In a single-phase circuit, capacitors are commonly employed for this purpose.
Function of Capacitors in Power Factor Correction
- Capacitors provide reactive power, which can counteract the inductive effects in a circuit.
- The presence of inductive loads (like motors) causes the current to lag behind the voltage, resulting in a low power factor.
Effects of Adding a Capacitor
1. Decrease in Line Current:
- Adding a capacitor reduces the total reactive power demand of the circuit.
- As reactive power is diminished, the overall current drawn from the supply reduces since the line current is proportional to the total apparent power (S = V * I).
2. Increase in Power Factor:
- The power factor (PF) is defined as the ratio of real power (P) to apparent power (S).
- By improving the balance between real and reactive power through the addition of capacitors, the power factor increases.
- A higher power factor indicates more efficient utilization of electrical power.
Conclusion
In summary, the use of a capacitor for power factor correction in a single-phase circuit effectively decreases the line current while simultaneously increasing the power factor. Hence, the correct answer is option 'A'. This enhancement leads to improved energy efficiency and reduced electricity costs in power distribution systems.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A capacitor used for power factor correction in single phase circuit decreases:a)the line current and increases power factorb)both line current and power factorc)line currentd)power factorCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























