UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > Consider an octahedral complex of the form [M...
Start Learning for Free
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+ with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?
- a)Three levels above and two below
- b)Two levels above and three below
- c)Five equally spaced levels
- d)No splitting, all the levels will coincide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the ...
- Crystal Field Splitting: This principle tells us how the interactions between the ligands and the central metal ion divide the d-orbitals into different energy levels. In an octahedral crystal field, such as seen in the coordination complex [Mn(H2O)6]3+, the field from six ligands will split the five degenerate d orbitals into two categories: two orbitals at a lower energy level (dxy, dxz, dyz typically denoted as t2g set) and three at a higher energy level (dz2, dx2−y2 typically denoted as eg set). This splitting accounts for the peculiar properties of coordination complexes like color and magnetism.
- High-spin and Low-spin Configurations: These concepts are related to the filling of the d-orbitals in transition metal complexes. In high-spin complexes, the electrons prefer to inhabit the higher energy orbitals (eg set) before they fully occupy the lower energy orbitals (t2g set) in order to minimize electron-electron repulsion (Hund's rule). Since the question specifies that this is a high-spin complex, that implies that this is the configuration we'll see for this complex.
- Ligand Field Stabilization Energy (LSFE): This concept refers to the stabilization of the system due to crystal field splitting. LFSE can vary when an electron is present at the lower or higher energy level, which influences the stability of a complex and its geometry.
- Electron Configuration of Mn³⁺: The electron configuration of Mn³⁺ is [Ar]3d⁴. Since this a high-spin complex, this means that there are four unpaired electrons, three of which will be in the eg level (higher energy level) and one will be in the t2g level (lower energy level).
In an octahedral complex, the degenerate d-orbital energy levels split into two sets because the ligand fields created by the coordinated ligands interact differently with the metal's d-orbitals, due to their spatial orientation.
The dx2-y2 and dz2 orbitals, known as eg orbitals, face the ligands on the axes, causing their energies to increase. The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, known as t2g orbitals, lie between the ligands and are lower in energy. Hence on an Orgel diagram, two levels (eg) will be higher and three (t2g) will be lower.
This splitting leads to two sets of degenerate levels: one lower energy t_set (three orbitals) and one higher energy eg set (two orbitals). In high-spin complexes of Mn3+, the available electrons populate the orbitals according to Hund's Rule, leading to as many parallel spins (unpaired electrons) as possible.
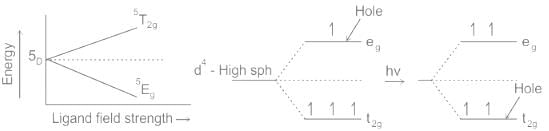
The dx2-y2 and dz2 orbitals, known as eg orbitals, face the ligands on the axes, causing their energies to increase. The dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals, known as t2g orbitals, lie between the ligands and are lower in energy. Hence on an Orgel diagram, two levels (eg) will be higher and three (t2g) will be lower.
This splitting leads to two sets of degenerate levels: one lower energy t_set (three orbitals) and one higher energy eg set (two orbitals). In high-spin complexes of Mn3+, the available electrons populate the orbitals according to Hund's Rule, leading to as many parallel spins (unpaired electrons) as possible.

Most Upvoted Answer
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the ...
Explanation:
1. Octahedral Complex [Mn(H2O)6]3+
- The given complex [Mn(H2O)6]3+ has an octahedral geometry with manganese (Mn) in the +3 oxidation state.
- This means that the Mn ion has a d4 electron configuration.
2. Orgel Diagram
- In an Orgel diagram, the d-orbital splitting of an octahedral complex is represented.
- For a high-spin d4 octahedral complex, the d-orbitals are split into two levels above and three levels below the average energy level.
3. Correct Answer - Option 'B'
- The correct representation of the d-orbital splitting for the [Mn(H2O)6]3+ complex in an Orgel diagram would show two levels above the average energy level and three levels below.
- This splitting pattern is characteristic of a high-spin d4 octahedral complex.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Two levels above and three below.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Similar UGC NET Doubts
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider an octahedral complex of the form [Mn(H2O)6]3+with Mn in the +3 oxidation state. If we represent this high-spin complex on an Orgel diagram, how will the d-orbital splitting appear?a)Three levels above and two belowb)Two levels above and three belowc)Five equally spaced levelsd)No splitting, all the levels will coincideCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























