Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > Two different types of chromatin can emerge f...
Start Learning for Free
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so.
The subsequent options are suggested.
P. The gene in (A) is repressed
Q. The gene in (B) is repressed
R. The gene in (A) is active
S. The gene in (B) is active
Which of the following sets is correct?
- a)P and S
- b)P and Q
- c)Q and S
- d)R and S
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (soleno...
Concept:
- The structure of the 30-nm fibre is a key element in understanding chromatin compaction.
- It consists of a helical array of nucleosomes, each comprising a core particle wrapping ∼146 or 147 base pairs (bp) of DNA associated with a linker histone.
- The globular domain of the linker histone constrains an additional ∼20 bp and the resulting chromosomes are connected by stretches of linker DNA with lengths varying between 0 and ∼70 bp.
- The main feature of solenoid model is that nucleosomes follow each other along the same helical path, and interactions between the histone cores occur sequentially.
Explanation:Fig 1: Chromatin compaction
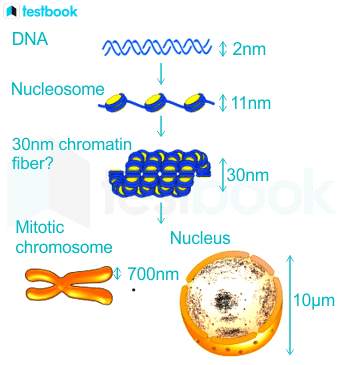
- Transitions between the 30-nm and 10-nm fibers are thought to be essential for the control of chromatin transcriptional status.
- However, recent studies demonstrate that in the nuclei, DNA is packed in tightly associated 10-nm fibers that are not compacted into 30-nm fibers.
- Additionally, the accessibility of DNA in chromatin depends on the local mobility of nucleosomes rather than on decompaction of chromosome regions.
Statement P:
The gene in (A) is repressed
- In gene (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin which can have effects on the gene.
- Nucleosome positioning is critical for gene expression and most DNA-related processes.
- While most genomic DNA is occupied by nucleosomes, many functional regions (promoters, enhancers, terminators) are depleted of nucleosomes (i.e. have low occupancy) and some regions are largely nucleosome-free.
- Nucleosome occupancy and positioning are critical to biological outcomes primarily because nucleosomes inhibit the access of other DNA-binding proteins to the DNA.
- A special class of “pioneer” transcription factors (e.g. FoxA and GATA) can bind their target sites in the context of nucleosomal DNA.
- Such pioneer factors, via recruitment of nucleosome remodelers, can open up the local chromatin, thereby facilitating the binding of other transcription factors that otherwise would be blocked by nucleosomes.
- The TATA-binding protein, and hence the entire basic RNA polymerase II transcription machinery, is virtually unable to bind nucleosomal DNA, and hence requires a nucleosome-free region to bind core promoters and initiate transcription.
- thus this statement is true.
Statement Q:
The gene in (B) is repressed.
- In the gene(B), histone H1 occupies the promoter region which has its effects on the transcription of the gene
- Active and repressed genomic regions are characterized by different profiles of histone modifications.
- H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 histones assemble as an octamer and wrap DNA.
- Each histone is composed of a C-terminal globular domain and an N-terminal tail domain.
- This tail domain is unstructured and flexible, so this feature allows the histone tail to be altered by various epigenetic modifiers, which function as a major component of gene expression regulation, thereby controlling a number of biological processes such as proliferation, DNA replication, and cellular death.
- There are several epigenetic modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation, which all have distinct biological functions
- Acetylation usually occurs on lysine residues, neutralizing their positive charge and thereby causing histones to drift away from DNA, which has a negative charge.
- The released structure facilitates access to transcriptional machinery such as transcription factors and RNA polymerase II.
- Thus, acetylation induces and enhances gene expression in general. Histone acetylation and deacetylation are catalyzed by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and HDACs, respectively.
- Histone demethylase reverses methylation of histones.
- Methylation activates or represses gene expression depending on which residue is methylated
- thus this statement is not true
Statement R:
The gene in (A) is active- Consider the explanation above thus this option is not true
Statement S:
The gene in (B) is active
- Consider the explanation above thus this option is true, asActive and repressed genomic regions are characterized by different profiles of histone modifications
hence the correct answer is option 1
Most Upvoted Answer
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (soleno...
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'A' which states that the gene in form (A) is active. Let's break down the explanation:
Chromatin Structure:
- Chromatin can exist in two different forms - one with a nucleosome occupying the gene's promoter (form A) and the other with histone H1 occupying the gene's promoter (form B).
- Form A is associated with an open chromatin structure, while form B is associated with a more condensed chromatin structure.
Gene Activity:
- In form A, where a nucleosome occupies the gene's promoter in an open chromatin structure, the gene is likely to be active.
- The presence of a nucleosome at the promoter region in an open chromatin structure allows for accessibility of transcription factors and RNA polymerase, leading to gene expression.
Conclusion:
- Therefore, based on the given information, it can be concluded that the gene in form A is active. This is because an open chromatin structure with a nucleosome at the promoter region allows for gene expression.
The correct answer is option 'A' which states that the gene in form (A) is active. Let's break down the explanation:
Chromatin Structure:
- Chromatin can exist in two different forms - one with a nucleosome occupying the gene's promoter (form A) and the other with histone H1 occupying the gene's promoter (form B).
- Form A is associated with an open chromatin structure, while form B is associated with a more condensed chromatin structure.
Gene Activity:
- In form A, where a nucleosome occupies the gene's promoter in an open chromatin structure, the gene is likely to be active.
- The presence of a nucleosome at the promoter region in an open chromatin structure allows for accessibility of transcription factors and RNA polymerase, leading to gene expression.
Conclusion:
- Therefore, based on the given information, it can be concluded that the gene in form A is active. This is because an open chromatin structure with a nucleosome at the promoter region allows for gene expression.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Similar Software Development Doubts
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two different types of chromatin can emerge from a 30 nm fibre (solenoid) in eukaryotic chromatin. In one form (A), a nucleosome occupies a gene's promoter within the open chromatin, whereas in the other (B), histone H1 does so. The subsequent options are suggested. P. The gene in (A) is repressed Q. The gene in (B) is repressed R. The gene in (A) is active S. The gene in (B) is active Which of the following sets is correct?a)P and Sb)P and Qc)Q and Sd)R and SCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























