Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > The hybridization state in triangle bipyramid...
Start Learning for Free
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:
- a)sp
- b)sp3d
- c)sp3
- d)sp2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp...
Carbonium ion methonium, CH5+ is produced by the addition of H+ to CH4. In CH5+ three hydrogen atoms are in a plane and one above and one below the plane.
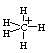
So its sp3d and the shape is trigonal bipyramid.
But this compound is considered a CH3+ carbenium ion with a molecule of hydrogen interacting with the empty orbital in a 3-center-2-electron bond. As the two hydrogen atoms in H2 are in continuously exchange positions with the three hydrogen atoms in the CH3+ methonium CH5+ is considered as a fluxional molecule. Due to the existence of CH3+ this is sp2 hybridised.
Most Upvoted Answer
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp...
There is a pure p orbital remaining perpendicular to the trigonal planar geometry...I may wrong.. please check my concept
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp...
Explanation:
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5 is SP2.
- Hybridization: Hybridization is the process of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that have different properties from the original orbitals. The hybridization state of an atom is determined by the number of hybrid orbitals it forms.
- Triangle bipyramidal geometry: Triangle bipyramidal geometry is a type of molecular geometry where a central atom is surrounded by five ligands. The arrangement of these ligands is such that there are three atoms in the equatorial plane and two atoms in the axial positions.
- CH5: CH5 is a hypothetical molecule that is not stable. However, it can be used as an example to understand the hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal geometry.
- Hybridization state in CH5: In CH5, the central carbon atom is surrounded by five hydrogen atoms. The carbon atom has four valence electrons, which means it needs four hybrid orbitals to form four covalent bonds with the hydrogen atoms.
- To form four hybrid orbitals, the carbon atom undergoes sp2 hybridization. This means that one s orbital and two p orbitals of the carbon atom are mixed to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals.
- These sp2 hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds with the hydrogen atoms in the equatorial plane. The remaining two p orbitals of the carbon atom form pi bonds with the hydrogen atoms in the axial positions.
- Therefore, the hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5 is sp2.
- Note: It is important to note that CH5 is not a stable molecule, and the actual hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal molecules may vary depending on the specific molecule.
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5 is SP2.
- Hybridization: Hybridization is the process of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that have different properties from the original orbitals. The hybridization state of an atom is determined by the number of hybrid orbitals it forms.
- Triangle bipyramidal geometry: Triangle bipyramidal geometry is a type of molecular geometry where a central atom is surrounded by five ligands. The arrangement of these ligands is such that there are three atoms in the equatorial plane and two atoms in the axial positions.
- CH5: CH5 is a hypothetical molecule that is not stable. However, it can be used as an example to understand the hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal geometry.
- Hybridization state in CH5: In CH5, the central carbon atom is surrounded by five hydrogen atoms. The carbon atom has four valence electrons, which means it needs four hybrid orbitals to form four covalent bonds with the hydrogen atoms.
- To form four hybrid orbitals, the carbon atom undergoes sp2 hybridization. This means that one s orbital and two p orbitals of the carbon atom are mixed to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals.
- These sp2 hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds with the hydrogen atoms in the equatorial plane. The remaining two p orbitals of the carbon atom form pi bonds with the hydrogen atoms in the axial positions.
- Therefore, the hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5 is sp2.
- Note: It is important to note that CH5 is not a stable molecule, and the actual hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal molecules may vary depending on the specific molecule.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The hybridization state in triangle bipyramidal CH5+ is:a)spb)sp3dc)sp3d)sp2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















