Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material,...
Start Learning for Free
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal to
- a)(G + 3K)/9KG
- b)(3G + K)/9KG
- c)9KG(G + 3K)
- d)9KG/(K + 3G)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticit...
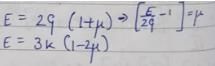
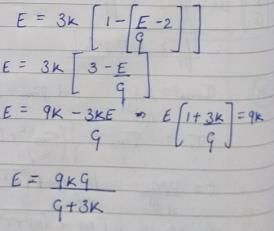
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticit...
Understanding Elastic Moduli Relationships
In the study of materials, particularly in civil engineering, it is essential to understand how different elastic moduli relate to one another. For homogeneous and isotropic materials, the relationship between the modulus of elasticity (E), the shear modulus (G), and the bulk modulus (K) can be derived from fundamental principles.
Key Definitions
- Modulus of Elasticity (E): Represents the stiffness of a material under uniaxial stress.
- Shear Modulus (G): Measures the material's response to shear stress.
- Bulk Modulus (K): Indicates how incompressible a material is under uniform pressure.
Deriving the Relationship
The relationship between E, G, and K can be expressed through the following equations:
1. Basic Equations:
- E = 3K(1 - 2ν)
- G = E / [2(1 + ν)]
- K = E / [3(1 - 2ν)]
Here, ν represents Poisson's ratio, which relates lateral strain to axial strain.
2. Substitution:
By manipulating these equations, we can express E in terms of G and K.
Final Expression
The expression derived for E in terms of G and K is:
E = 9KG / (K + 3G)
This relationship shows how the bulk and shear moduli contribute to the overall elasticity of the material.
Conclusion
The correct answer to the initial question is option 'C':
9KG(G + 3K)
This highlights an important relationship in material science, enabling engineers to predict and analyze material behavior under various loading conditions. Understanding these relationships is crucial for designing safe and effective structures.
In the study of materials, particularly in civil engineering, it is essential to understand how different elastic moduli relate to one another. For homogeneous and isotropic materials, the relationship between the modulus of elasticity (E), the shear modulus (G), and the bulk modulus (K) can be derived from fundamental principles.
Key Definitions
- Modulus of Elasticity (E): Represents the stiffness of a material under uniaxial stress.
- Shear Modulus (G): Measures the material's response to shear stress.
- Bulk Modulus (K): Indicates how incompressible a material is under uniform pressure.
Deriving the Relationship
The relationship between E, G, and K can be expressed through the following equations:
1. Basic Equations:
- E = 3K(1 - 2ν)
- G = E / [2(1 + ν)]
- K = E / [3(1 - 2ν)]
Here, ν represents Poisson's ratio, which relates lateral strain to axial strain.
2. Substitution:
By manipulating these equations, we can express E in terms of G and K.
Final Expression
The expression derived for E in terms of G and K is:
E = 9KG / (K + 3G)
This relationship shows how the bulk and shear moduli contribute to the overall elasticity of the material.
Conclusion
The correct answer to the initial question is option 'C':
9KG(G + 3K)
This highlights an important relationship in material science, enabling engineers to predict and analyze material behavior under various loading conditions. Understanding these relationships is crucial for designing safe and effective structures.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a homogeneous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal toa)(G + 3K)/9KGb)(3G + K)/9KGc)9KG(G + 3K)d)9KG/(K + 3G)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























