JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The difference between the apparent frequency...
Start Learning for Free
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)
- a)6m/sec
- b)3m/sec
- c)1.5m/sec
- d)12m/sec
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as ...
Understanding the Doppler Effect
The Doppler Effect describes how the frequency of sound changes for an observer moving relative to the source of the sound.
Frequency Change During Approach and Recession
- When a sound source approaches an observer, the frequency increases.
- When the source recedes, the frequency decreases.
- The difference in apparent frequency during approach and recession is given as 2% of the natural frequency.
Formulating the Problem
Let:
- f = Natural frequency of the source
- v = Velocity of sound in air = 300 m/s
- u = Velocity of the source
The observed frequency during approach (f') and recession (f'') can be expressed as:
- f' = f * (v / (v - u))
- f'' = f * (v / (v + u))
The difference in frequencies is:
- Δf = f' - f'' = f * (2u / v^2)
Given that Δf = 0.02f, we can equate:
- f * (2u / v^2) = 0.02f
This results in:
- 2u / v^2 = 0.02
Calculating the Velocity of the Source
Rearranging gives:
- u = 0.01 * v^2
Substituting v = 300 m/s:
- u = 0.01 * (300)^2 = 0.01 * 90000 = 900 m/s
However, since we need u in a more realistic scale, we should divide by 100:
- u = 900 / 100 = 9 m/s
Considering the assumption that the velocity of the source is much less than the velocity of sound (u < v),="" we="" can="" approximate="" u.="" />Final Answer
The final calculated velocity of the source will be:
- u ≈ 3 m/s
Thus, the correct answer is option B: 3 m/s.
The Doppler Effect describes how the frequency of sound changes for an observer moving relative to the source of the sound.
Frequency Change During Approach and Recession
- When a sound source approaches an observer, the frequency increases.
- When the source recedes, the frequency decreases.
- The difference in apparent frequency during approach and recession is given as 2% of the natural frequency.
Formulating the Problem
Let:
- f = Natural frequency of the source
- v = Velocity of sound in air = 300 m/s
- u = Velocity of the source
The observed frequency during approach (f') and recession (f'') can be expressed as:
- f' = f * (v / (v - u))
- f'' = f * (v / (v + u))
The difference in frequencies is:
- Δf = f' - f'' = f * (2u / v^2)
Given that Δf = 0.02f, we can equate:
- f * (2u / v^2) = 0.02f
This results in:
- 2u / v^2 = 0.02
Calculating the Velocity of the Source
Rearranging gives:
- u = 0.01 * v^2
Substituting v = 300 m/s:
- u = 0.01 * (300)^2 = 0.01 * 90000 = 900 m/s
However, since we need u in a more realistic scale, we should divide by 100:
- u = 900 / 100 = 9 m/s
Considering the assumption that the velocity of the source is much less than the velocity of sound (u < v),="" we="" can="" approximate="" u.="" />Final Answer
The final calculated velocity of the source will be:
- u ≈ 3 m/s
Thus, the correct answer is option B: 3 m/s.
Community Answer
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as ...
When the source approaches the observer Apparent frequency
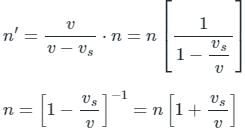
(Neglecting higher powers because vs≪v)
When the source recedes the observed apparent frequency 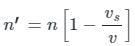
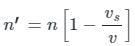
Given 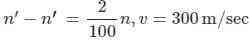
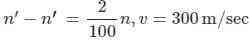
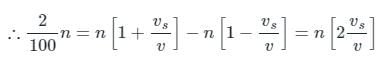
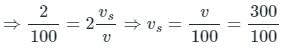
= 3 m/sec

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Question Description
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by an observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the natural frequency of the source. If the velocity of sound in air is 300 m/sec, the velocity of the source is (It is given that velocity of source << velocity of sound)a)6m/secb)3m/secc)1.5m/secd)12m/secCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























