Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Ele...
Start Learning for Free
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :
- a)Electrophilic substitution
- b)Electrophilic addition
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Nucleophilic addition
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)...
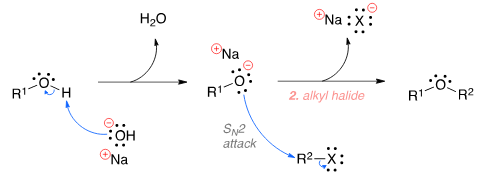
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction used to convert an alcohol and an alkyl halide to an ether using a base such as NaOH. The mechanism begins with the base abstracting the proton from the alcohol to form an alkoxide intermediate. The alkoxide then attacks the alkyl halide in a nucleophilic substi-tution reaction (SN2), which results in the formation of the final ether product and a metal halide by-product.
View all questions of this test

Most Upvoted Answer
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)...
Williamson's synthesis takes place by nucleophilic substitution reaction(SN2)
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)...
Williamson's synthesis is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction involves the substitution of one nucleophile with another in a chemical compound. The reaction is named after Alexander Williamson, who first described this method of synthesis in 1850.
Reaction mechanism:
The reaction involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with an alkyl halide to form an ether. Here is the general mechanism for Williamson's synthesis:
1. Formation of alkoxide ion: The alkoxide ion is formed by deprotonation of an alcohol using a strong base, typically sodium or potassium hydroxide. The alkoxide ion is a strong nucleophile.
2. Nucleophilic attack: The alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom of an alkyl halide. The alkyl halide is an electrophile due to the polarity of the carbon-halogen bond.
3. Substitution: The nucleophilic attack results in the displacement of the halogen atom by the alkoxide ion. The product formed is an ether, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups.
Example:
Let's consider the synthesis of ethyl methyl ether using Williamson's synthesis. The reaction is as follows:
CH3Br + NaOCH2CH3 → CH3OCH2CH3 + NaBr
In this reaction, sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3) is prepared by reacting ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) with sodium hydroxide. The sodium ethoxide then reacts with methyl bromide (CH3Br) to form ethyl methyl ether (CH3OCH2CH3) and sodium bromide (NaBr).
Significance:
Williamson's synthesis is a widely used method for the preparation of ethers. Ethers are important functional groups in organic chemistry and find applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and solvents. This method allows for the synthesis of symmetrical ethers (where both alkyl groups are the same) and mixed ethers (where alkyl groups are different).
Summary:
In summary, Williamson's synthesis is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction. It involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with an alkyl halide to form an ether. This method is widely used for the synthesis of ethers and is named after Alexander Williamson, who first described this reaction in 1850.
Reaction mechanism:
The reaction involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with an alkyl halide to form an ether. Here is the general mechanism for Williamson's synthesis:
1. Formation of alkoxide ion: The alkoxide ion is formed by deprotonation of an alcohol using a strong base, typically sodium or potassium hydroxide. The alkoxide ion is a strong nucleophile.
2. Nucleophilic attack: The alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom of an alkyl halide. The alkyl halide is an electrophile due to the polarity of the carbon-halogen bond.
3. Substitution: The nucleophilic attack results in the displacement of the halogen atom by the alkoxide ion. The product formed is an ether, which contains an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups.
Example:
Let's consider the synthesis of ethyl methyl ether using Williamson's synthesis. The reaction is as follows:
CH3Br + NaOCH2CH3 → CH3OCH2CH3 + NaBr
In this reaction, sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3) is prepared by reacting ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) with sodium hydroxide. The sodium ethoxide then reacts with methyl bromide (CH3Br) to form ethyl methyl ether (CH3OCH2CH3) and sodium bromide (NaBr).
Significance:
Williamson's synthesis is a widely used method for the preparation of ethers. Ethers are important functional groups in organic chemistry and find applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and solvents. This method allows for the synthesis of symmetrical ethers (where both alkyl groups are the same) and mixed ethers (where alkyl groups are different).
Summary:
In summary, Williamson's synthesis is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction. It involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with an alkyl halide to form an ether. This method is widely used for the synthesis of ethers and is named after Alexander Williamson, who first described this reaction in 1850.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Williamsons synthesis is an example of :a)Electrophilic substitutionb)Electrophilic additionc)Nucleophilic substitution reactiond)Nucleophilic additionCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















